2018 Hyundai Elantra Repair Manual Guide
When it comes to keeping a car running smoothly, knowing where to start can make all the difference. Regular upkeep is key to ensuring longevity, efficiency, and performance. With the right guidance, even complex systems can become manageable, allowing drivers to tackle issues that arise and keep their car in top shape.
This guide covers essential maintenance insights, offering detailed instructions and helpful tips for both routine and advanced care. Whether you’re addressing mechanical problems, performing diagnostics, or simply looking to enhance your understanding of vehicle systems, this resource provides the expertise and knowledge needed to maintain optimal performance.
Explore various sections dedicated to upkeep strategies, common troubleshooting methods, and in-depth explanations of mechanical and electrical components. Essential for both novices and experienced drivers, this guide is structured to help you gain confidence in handling your vehicle’s unique demands, making it easier to enjoy a safe and reliable driving experience.
Comprehensive Guide to 2018 Hyundai Elantra Repair
This section provides an in-depth approach to vehicle maintenance, aiming to help car owners understand essential service tasks, common mechanical issues, and diagnostic tips. Regular upkeep enhances both the performance and longevity of your automobile, reducing the risk of more serious complications. Following these steps will help you maintain a reliable and efficient vehicle while ensuring safe and smooth driving experiences.
Routine Maintenance Checklist
- Check and replace engine oil and filter every few thousand miles.
- Inspect brake pads for wear and replace if necessary to ensure safe braking.
- Examine the battery’s terminals and cables for corrosion and secure connections.
- Rotate tires regularly for even tread wear, which extends tire life.
- Flush and refill coolant at recommended intervals to prevent engine overheating.
- Replace windshield wipers annually or as needed for clear visibility in adverse weather.
Addressing Common Mechanical Issues
- Engine Misfiring: Check spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors, as these are common causes of irregular combustion.
- Transmission Slippage: Low fluid levels or dirty fluid can cause transmission issues; consider a fluid replacement if you experience delays in shifting.
- Brake Noise: Squealing or grinding sounds often indicate worn pads or rotors that need immediate attention to maintain braking efficiency.
- Suspension Issues: Listen for clunks or rattling sounds while driving over bumps, which may indicate worn-out suspension components.
- Heating and Cooling Problems: Inspect the AC compressor, refrigerant levels, and thermostat, as these components often contribute to temperature inconsistencies.
Diagnostic Tips and Tools
To effectively troubleshoot, consider using an OBD-II scanner to identify error codes related to engine performance and other systems. Follow these tips for accurate diagnostics:
- Always record the error codes before resetting the system for future reference.
- Cross-check code definitions to narrow down potential problem sources.
- After addressing any issues, test-drive to confirm repairs resolved the symptoms.
By following this comprehensive guide, owners can approach maintenance and troubleshooting with confidence, ensuring a smooth driving experience and reducing the
Identifying Common Issues in Hyundai Elantra
Understanding common mechanical and electrical issues can help owners maintain their vehicles and address any emerging concerns early. This section outlines typical problems observed across key systems, offering insights for diagnostics and preventive measures.
- Engine Performance Issues
- Inconsistent idling or sudden stalling may point to faulty sensors or fuel system blockages.
- Unusual engine noises, especially knocking, could signal issues with ignition timing or the need for oil replacement.
- Transmission Challenges
- Difficulty shifting gears or unexpected jerks while accelerating may stem from fluid issues or worn clutch components.
- Lagging responses in automatic models often indicate a need for transmission fluid check or software recalibration.
- Electrical System Malfunctions
- Persistent battery drain or flickering dashboard lights can be symptoms of grounding issues or alternator malfunction.
- Intermittent problems with power windows or locks may result from wiring wear or weak connections.
- Suspension and Steering Concerns
- Excessive vibrations or unusual sounds during turns often indicate worn-out suspension bushings or ball joints.
- Steering that feels heavy or less responsive can be a sign of low power steering fluid or misaligned wheels.
- Brake System Wear
- Squealing or grinding noises suggest worn brake pads or the need for rotor inspection.
- A soft or sinking brake pedal may indicate air in the brake lines or fluid leakage.
By recognizing these signs and seeking timely solutions, vehicle owners can enhance reliability and extend the lifespan of their cars.
Essential Tools for Elantra Repairs

Equipping yourself with the right tools is crucial to maintaining and servicing your vehicle effectively. Whether you’re handling simple maintenance tasks or diving into more intricate fixes, having a reliable set of tools ensures precision and saves time.
- Socket Set: A comprehensive socket set is essential for loosening and tightening bolts, especially in tight spaces. Choose a set with both metric and standard sizes for versatility.
- Torque Wrench: Maintaining accurate torque specifications is key to preventing overtightening. A torque wrench allows you to apply the precise amount of force needed for each bolt.
- Screwdriver Set: A variety of flathead and Phillips screwdrivers will cover most small components. Magnetic tips can help with handling small screws.
- Jack and Jack Stands: For undercarriage work, a reliable jack and sturdy stands provide the necessary lift and stability, allowing safe access beneath the vehicle.
- Multimeter: Essential for diagnosing electrical issues, a digital multimeter tests circuits, voltage levels, and battery health, helping locate electrical faults quickly.
- Brake Bleeder Kit: When replacing brake components, a bleeder kit removes air from the brake lines, ensuring a firm brake pedal and safe operation.
- Oil Filter Wrench: Changing the oil filter becomes easier with a proper wrench, designed to grip and remove the filter without hassle.
- OBD-II Scanner: An OBD-II scanner is invaluable for reading diagnostic trouble codes, enabling efficient troubleshooting for any warning lights or performance issues.
These fundamental tools form a well-rounded kit for handling most maintenance tasks and repairs. Investing in high-quality tools can enhance your work, ensuring reliability and extending your vehicle’s performance.
Step-by-Step Engine Maintenance Guide
Regular engine maintenance is crucial for ensuring long-term performance, fuel efficiency, and overall vehicle health. This guide provides a structured approach to essential engine care tasks that can help prevent costly repairs and prolong the life of the engine. By following these steps, you’ll be able to address common issues proactively, keep the engine running smoothly, and maintain optimal performance.
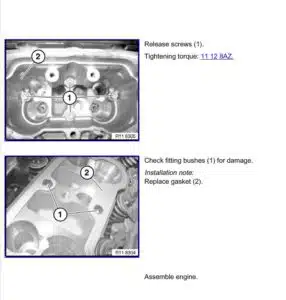
1. Checking and Replacing Engine Oil
Engine oil plays a vital role in reducing friction and maintaining smooth engine operation. Begin by inspecting the oil level using the dipstick. Ensure the oil is within the recommended range, topping up if necessary. Changing the oil every 5,000 to 7,500 miles–or as recommended by your vehicle’s service interval–is essential. When changing oil, always replace the oil filter to avoid contamination and ensure the engine receives clean lubrication.
2. Inspecting and Replacing Air Filters

The air filter prevents dirt, dust, and debris from entering the engine, which can affect its efficiency. A clogged or dirty air filter restricts airflow and can reduce engine performance. Inspect the air filter regularly, and replace it if it appears dusty or damaged. For most cars, changing the air filter every 15,000 to 30,000 miles is recommended, but this interval may vary based on driving conditions.
Following these basic steps can make a significant difference in maintaining engine health, extending its life, and keeping your vehicle running at peak efficiency.
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
Electrical issues in vehicles can lead to various malfunctions that disrupt normal operations, from non-responsive lights to failing starting systems. Understanding common signs and symptoms of electrical faults can help identify problems early and minimize downtime.
To address electrical concerns effectively, it’s essential to break down the system into key components such as the battery, alternator, fuses, and wiring connections. This guide will help pinpoint typical issues in each area, allowing for a systematic approach to diagnosing and fixing electrical faults.
- Battery Check: Begin by inspecting the battery’s terminals for corrosion or loose connections. Ensure the battery holds a stable charge and is not over-aged, as older batteries lose efficiency and cause irregular power flow.
- Alternator Output: The alternator is crucial for recharging the battery and supplying power to other systems. Use a multimeter to check for consistent voltage output. A low reading may indicate a need for alternator servicing or replacement.
- Fuses and Relays: Inspect the fuse box for blown fuses or damaged relays, which can cause intermittent or complete loss of power to certain systems. Replace any defective fuses or relays as necessary.
- Wiring and Connectors: Frayed wires or loose connectors are common sources of electrical issues. Trace wiring for visible damage or weak connections, especially in areas exposed to wear. Tighten any loose connectors and repair damaged wires.
Following a logical sequence when checking each component helps in pinpointing the exact cause of the problem, saving time and preventing unnecessary repairs. Always handle electrical parts carefully to avoid further complications or safety risks.
Transmission Repair Tips for Beginners
Working on the gearbox of a vehicle can seem daunting, especially for those new to automotive maintenance. However, with the right approach and knowledge, it can be an accessible and rewarding task. This section provides essential guidance for novices looking to gain confidence and skills in managing transmission-related issues.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the intricacies of the gearbox, familiarize yourself with its components and functions. Learn about the transmission types, such as automatic and manual, and understand how they operate. This foundational knowledge will help you diagnose problems more effectively and determine the necessary steps for resolution.
Essential Tools and Safety Precautions
Equipping yourself with the right tools is crucial for any repair task. Basic tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and a jack will be essential. Additionally, always prioritize safety by wearing protective gear and ensuring the vehicle is securely lifted before starting any work. Understanding safety protocols will help you work more confidently and efficiently.
How to Replace Brake Components

Maintaining optimal performance of your vehicle’s stopping system is crucial for safety and efficiency. Over time, brake parts can wear out, requiring replacement to ensure reliable operation. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to help you effectively swap out these essential components.
Before beginning the process, gather all necessary tools and components, including a jack, lug wrench, brake pads, rotors, and brake fluid. It is important to work on a level surface and ensure the vehicle is securely lifted before proceeding.
1. Lift the Vehicle: Use a jack to elevate the vehicle and place jack stands for added safety. This step is vital to provide ample space to work on the braking system.
2. Remove the Wheel: Loosen the lug nuts using a lug wrench, then remove the wheel to access the brake assembly. Keep the lug nuts in a safe place for reinstallation.
3. Inspect Existing Components: Examine the current brake pads and rotors for wear. If they show signs of excessive wear or damage, proceed with their replacement.
4. Remove Old Brake Pads: Locate the caliper, which holds the brake pads in place. Use appropriate tools to detach the caliper from its bracket, allowing you to access the worn pads. Carefully slide them out, taking note of their orientation for installing new ones.
5. Replace Rotors: If the rotors are worn or warped, they should also be replaced. Remove any retaining screws and slide the old rotor off the hub. Position the new rotor onto the hub, ensuring it fits securely.
6. Install New Brake Pads: Apply a thin layer of brake grease to the back of the new pads to prevent noise. Position the pads into the caliper bracket, following the orientation of the old pads.
7. Reattach the Caliper: Carefully position the caliper back over the new pads and secure it using the appropriate bolts. Ensure everything is tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
8. Reinstall the Wheel: Place the wheel back onto the hub and hand-tighten the lug nuts. Lower the vehicle and then fully tighten the lug nuts in a crisscross pattern to ensure even pressure.
9. Test the Brakes: Before driving, pump the brake pedal several times to ensure proper engagement of the pads against the rotors. Check the brake fluid level and top it up if necessary.
Regular maintenance of braking components is essential for safe driving. By following these steps, you can ensure that your vehicle’s stopping system remains in top condition.
DIY Suspension and Steering Fixes
Addressing issues related to the suspension and steering system can significantly enhance vehicle performance and safety. This section aims to empower car enthusiasts with practical solutions for common problems that may arise over time. By following straightforward steps, you can restore your vehicle’s handling and ride quality without the need for professional assistance.
Identifying Common Issues
Before attempting any repairs, it’s essential to recognize the signs of wear and tear in your vehicle’s suspension and steering components. Common indicators include unusual noises while driving, uneven tire wear, and a noticeable decrease in handling responsiveness. Once identified, you can take the necessary steps to address these issues effectively.
Essential Tools and Parts
To perform maintenance or repairs on your suspension and steering systems, having the right tools is crucial. Below is a list of essential tools and parts that you may need for your DIY project:
| Tool/Part | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Jack and Jack Stands | To lift and secure the vehicle for safe access to components. |
| Wrench Set | For loosening and tightening nuts and bolts. |
| Torque Wrench | To ensure bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. |
| Ball Joint Separator | For removing and replacing ball joints safely. |
| Replacement Parts | Such as bushings, tie rod ends, or shock absorbers as needed. |
Fuel System Maintenance Essentials
Proper upkeep of the fuel delivery system is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. Regular attention to this vital component not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the risk of costly repairs down the line. Understanding key maintenance practices can help keep the system functioning smoothly, thus contributing to the overall reliability of the vehicle.
Key Components to Monitor

- Fuel Filter: Regularly replacing the fuel filter is essential to prevent contaminants from clogging the fuel lines and damaging the injectors.
- Fuel Injectors: Periodic cleaning of fuel injectors ensures that fuel is delivered uniformly to the engine, improving combustion efficiency.
- Fuel Pump: Monitoring the fuel pump for signs of wear can prevent performance issues and maintain adequate fuel pressure.
Maintenance Practices
- Check and replace the fuel filter at the manufacturer-recommended intervals.
- Use fuel injector cleaner as part of regular maintenance to remove deposits.
- Inspect fuel lines for leaks or damage, and replace as necessary.
- Ensure that the fuel tank is kept at least a quarter full to prevent sediment from being drawn into the fuel system.
Implementing these practices can significantly enhance the performance of the fuel delivery system, ensuring that the engine operates efficiently and effectively over time.
Diagnosing Air Conditioning Issues

When the climate control system in a vehicle fails to provide the expected comfort, it can lead to an uncomfortable driving experience. Identifying the root causes of these malfunctions is crucial for restoring optimal functionality. This section focuses on common problems associated with air conditioning systems and offers insights into effective troubleshooting techniques.
Common Symptoms of Malfunction
One of the first indicators of air conditioning trouble is inadequate cooling. Drivers may notice that the system fails to lower the cabin temperature effectively, despite the settings being adjusted. Additionally, unusual noises, such as hissing or clanking, can signal issues with internal components. Foul odors emanating from the vents may suggest mold or bacteria growth, which can impact air quality.
Troubleshooting Steps

To accurately diagnose these issues, start by checking the refrigerant levels. Low refrigerant can prevent the system from functioning properly, leading to reduced cooling capacity. If levels are adequate, inspect the compressor for any signs of damage or malfunction. Furthermore, ensure that the condenser and evaporator coils are clean and free from obstructions. Regular maintenance can help prevent many of these problems, ensuring that the climate control system operates smoothly.
Understanding Elantra’s Diagnostic Codes
Modern vehicles utilize a sophisticated system of codes that aid in identifying issues within the engine and other essential components. These codes serve as a crucial bridge between the vehicle’s onboard computer and the technician, allowing for efficient troubleshooting and repairs. By decoding these messages, owners can gain insights into their automobile’s performance and potential areas needing attention.
What Are Diagnostic Codes?
Diagnostic codes are alphanumeric sequences generated by the onboard computer when it detects an anomaly in the vehicle’s operation. These codes can be categorized into two main types:
- Generic Codes: Standardized codes applicable across various makes and models.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Unique codes that provide insights tailored to a specific make, offering more detailed information about particular systems.
How to Interpret the Codes
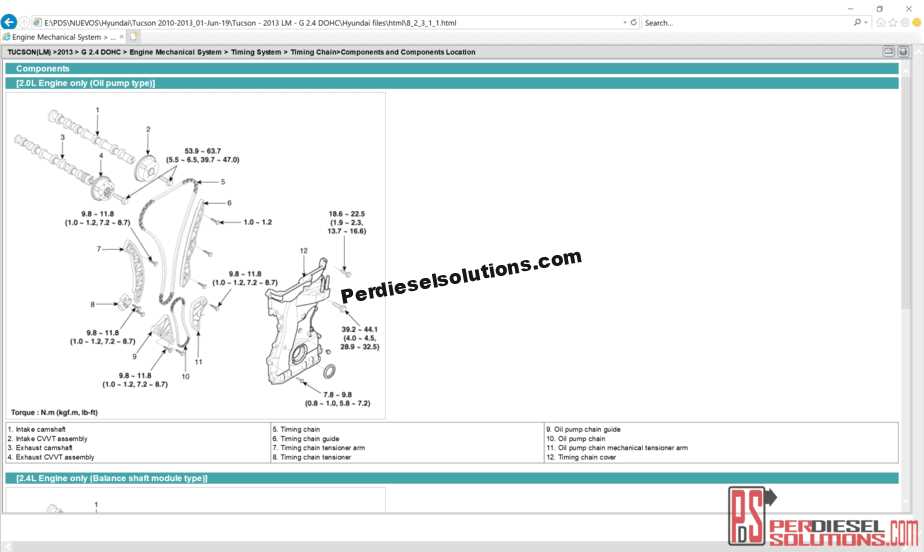
Once the codes are retrieved using a diagnostic scanner, understanding their meaning is essential for proper diagnosis. Here’s a simple approach to interpreting these codes:
- Identify the code format, typically starting with a letter followed by four digits.
- Refer to a comprehensive code database to find the corresponding definition.
- Evaluate the symptoms associated with the code to determine the potential root cause.
By mastering the interpretation of these diagnostic codes, vehicle owners can make informed decisions regarding maintenance and repairs, ultimately prolonging the life of their automobile.
Best Practices for Preventive Maintenance
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of any vehicle. By adhering to a systematic approach, owners can prevent potential issues, reduce repair costs, and enhance safety. Implementing preventive measures fosters a proactive mindset, enabling timely interventions before minor problems escalate into significant failures.
One effective strategy is to adhere to a consistent maintenance schedule. This includes regular checks of vital components, which can help identify wear and tear early on. Owners should consult the guidelines provided by manufacturers to determine appropriate intervals for inspections and servicing.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 5,000 to 7,500 miles | Ensures engine efficiency and prevents damage |
| Tire Rotation | Every 5,000 to 7,500 miles | Promotes even wear and extends tire life |
| Brake Inspection | Every 10,000 miles | Enhances safety and responsiveness |
| Fluid Checks | Monthly | Maintains optimal performance and prevents leaks |
| Battery Inspection | Every 6 months | Prevents unexpected breakdowns |
In addition to routine tasks, keeping records of maintenance activities is beneficial. Documenting services performed helps track the vehicle’s history and can be invaluable during future evaluations or resale. Furthermore, investing in quality parts and products enhances reliability and performance, contributing to the overall health of the automobile.