Comprehensive Guide to Repairing John Deere 310G

Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of heavy machinery is vital for any operator. Regular upkeep not only enhances performance but also minimizes the risk of costly breakdowns. This guide aims to provide essential insights into the processes involved in maintaining and troubleshooting specific models of construction equipment.
Understanding the intricacies of machinery care can significantly impact productivity on the job site. By familiarizing oneself with the key components and their functions, operators can identify potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach fosters a safer working environment and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
Additionally, having access to detailed instructions and guidelines empowers users to undertake maintenance tasks confidently. Whether it’s routine checks or more complex interventions, a well-structured reference can serve as a valuable tool for both novices and experienced operators alike. By investing time in proper care techniques, one can ensure that their equipment remains reliable and effective.
Overview of John Deere 310G
This section provides a comprehensive insight into a versatile construction machine known for its reliability and efficiency. Designed to tackle various tasks in the field, it combines power with user-friendly features, making it a favorite among operators and contractors alike.
Key Features
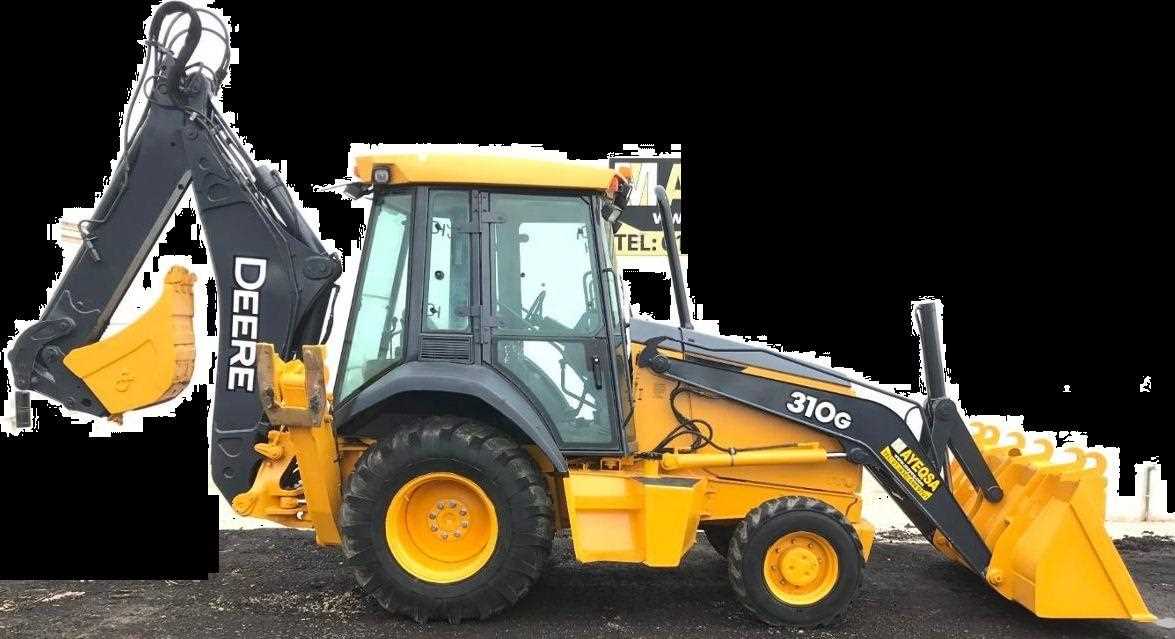

The machine boasts a robust engine that delivers exceptional performance, ensuring that heavy lifting and digging are completed with ease. Its hydraulic system enhances operational capabilities, while the ergonomic controls offer a seamless user experience.
Applications
Commonly utilized in construction, landscaping, and excavation projects, this equipment excels in a variety of environments. Its adaptability allows it to handle both large-scale tasks and smaller, precise operations effectively.
Common Issues with 310G Models
When operating heavy machinery, certain challenges frequently arise, impacting efficiency and functionality. Understanding these common problems can assist operators in maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential breakdowns.
- Hydraulic System Failures: Issues such as leaks or inconsistent pressure can hinder performance. Regular inspections are essential to ensure all connections and seals are intact.
- Engine Overheating: This can stem from insufficient coolant levels, clogged radiators, or malfunctioning thermostats. Keeping the cooling system clean and properly filled is crucial.
- Electrical Problems: Faulty wiring, blown fuses, or dead batteries can lead to operational disruptions. Routine checks of the electrical system can mitigate these risks.
- Transmission Difficulties: Slipping or harsh shifting may indicate low fluid levels or worn components. Monitoring fluid conditions and changing it regularly can prevent serious issues.
- Wear and Tear on Tires: Uneven wear can affect traction and stability. Regularly inspecting tire condition and alignment can prolong their lifespan.
Addressing these common concerns proactively can enhance the longevity and efficiency of your equipment, ensuring it remains a reliable asset in your operations.
Importance of a Repair Manual
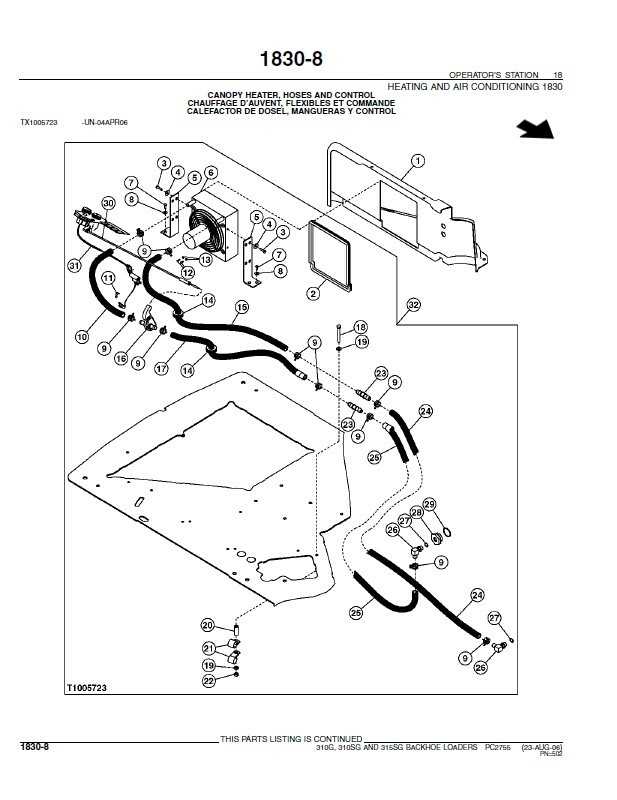
Having access to a comprehensive guide is crucial for anyone working with machinery. Such a resource serves as a valuable tool for troubleshooting, maintenance, and overall operational efficiency. It provides essential information that helps users understand the equipment’s components and functions, ensuring they can tackle issues effectively.
One key advantage of this type of documentation is the ability to perform tasks with confidence. With detailed instructions and diagrams at hand, operators can execute repairs and maintenance procedures accurately, minimizing the risk of errors. This not only extends the lifespan of the machinery but also enhances safety.
Moreover, a thorough guide fosters a deeper understanding of the equipment. Users become more familiar with its inner workings, which empowers them to identify potential problems before they escalate. This proactive approach can save time and reduce repair costs in the long run.
In summary, the significance of a well-structured reference resource cannot be overstated. It equips operators with the knowledge and skills necessary for effective management, ultimately contributing to smoother operations and improved productivity.
Essential Tools for Repair Tasks
Having the right instruments is crucial for effectively addressing various maintenance and service challenges. This section outlines the fundamental equipment necessary to ensure smooth operations and optimal results in any technical endeavor.
Basic Hand Tools
- Wrenches: A variety of sizes to fit different bolts and nuts.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips for versatility.
- Pliers: Essential for gripping, twisting, and cutting.
- Socket Set: For quick and efficient fastening.
Power Tools
- Drill: Useful for creating holes or driving screws.
- Angle Grinder: Perfect for cutting and shaping materials.
- Impact Wrench: Ideal for loosening stubborn fasteners.
- Reciprocating Saw: Great for demolition and cutting through various materials.
Equipping yourself with these tools can greatly enhance your efficiency and effectiveness in tackling maintenance projects.
Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
This section provides a comprehensive guide for tackling various maintenance tasks on your equipment. By following detailed instructions, you can ensure that each component functions optimally, enhancing overall performance and longevity.
1. Safety First: Before beginning any task, ensure you are equipped with the necessary safety gear. This includes gloves, goggles, and appropriate footwear to protect yourself from potential hazards.
2. Gather Tools and Materials: Collect all the required tools and replacement parts. Having everything on hand will streamline the process and reduce downtime.
3. Initial Assessment: Conduct a thorough inspection of the machinery. Identify any visible issues or irregularities that may require attention, and make notes for reference during the repair.
4. Disassembly: Carefully dismantle the components as per the outlined steps. Use the correct tools to avoid damaging parts. Organize screws and small pieces to facilitate reassembly.
5. Inspection and Cleaning: Once disassembled, inspect each part for wear or damage. Clean all components to remove dirt and debris that may hinder functionality.
6. Replacement of Parts: If any components are worn or damaged, replace them with new ones. Ensure compatibility with your equipment to maintain optimal performance.
7. Reassembly: Follow the reverse order of disassembly to reassemble the parts. Double-check that all components are securely fitted and that no tools are left inside the machinery.
8. Testing: Once reassembled, conduct a series of tests to ensure everything operates correctly. Monitor for any unusual sounds or performance issues that may need further attention.
9. Documentation: Keep a record of all maintenance performed, including dates and any parts replaced. This information is invaluable for future reference and can assist in identifying patterns over time.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Ensuring the extended lifespan of your equipment requires consistent attention and proactive measures. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule can significantly enhance performance and reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
Regular Inspections: Conduct thorough inspections at regular intervals. Look for signs of wear and tear, such as leaks or unusual noises. Early detection of potential issues can prevent more serious problems down the line.
Fluid Checks: Maintain proper fluid levels, including hydraulic fluid, oil, and coolant. Regularly checking and changing these fluids is crucial for optimal operation and can prevent overheating and excessive wear.
Filter Replacement: Replace air and fuel filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Clean filters ensure that your machine operates efficiently and can improve fuel economy.
Lubrication: Keep all moving parts well-lubricated to minimize friction and wear. Use high-quality lubricants and follow the suggested lubrication intervals to maintain smooth operation.
Battery Care: Inspect the battery for corrosion and ensure proper connections. Regularly charge the battery, especially during periods of inactivity, to avoid starting issues.
Operator Training: Ensure that all operators are trained in the proper use of the equipment. Understanding the capabilities and limitations can prevent misuse and reduce wear.
By following these essential tips, you can maximize the durability and performance of your machinery, ensuring it serves you well for years to come.
Electrical System Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to diagnosing issues within the electrical framework of heavy machinery. Understanding the intricacies of the electrical system is crucial for effective maintenance and ensuring optimal performance. This guide outlines common problems, symptoms, and solutions, empowering operators to identify and address faults efficiently.
Begin by inspecting the battery and its connections. Ensure that terminals are clean and tightly secured. A weak or dead battery is a frequent culprit in electrical failures. If the battery appears functional, check the alternator’s output to confirm it is charging correctly.
Next, examine wiring harnesses for signs of wear or damage. Frayed wires can cause shorts or intermittent connectivity, leading to erratic behavior. Use a multimeter to test continuity across the circuit, helping pinpoint specific areas of concern.
Additionally, consider the fuses and relays within the system. A blown fuse can interrupt power flow, while a faulty relay may prevent components from receiving the necessary signals. Replacing damaged fuses and testing relays can resolve many electrical issues.
Finally, consult the schematics of the electrical system for detailed information on component layout and function. This reference can aid in tracing connections and understanding the overall design, facilitating a more thorough investigation into any persistent problems.
Hydraulic System Maintenance Insights
Maintaining the hydraulic system of construction equipment is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular inspection and upkeep can prevent costly breakdowns and enhance efficiency. Understanding the core components and functions of this system is vital for operators and technicians alike.
Key maintenance tasks include checking fluid levels, inspecting hoses for wear, and ensuring that connections are secure. Additionally, monitoring the condition of filters is crucial, as they prevent contaminants from entering the system. A proactive approach to maintenance can significantly reduce the risk of hydraulic failures.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Level Check | Weekly | Ensure fluid is at recommended level to prevent overheating. |
| Hose Inspection | Monthly | Look for cracks or signs of wear to avoid leaks. |
| Filter Replacement | Every 500 hours | Replace to maintain clean fluid flow and system efficiency. |
| Fluid Quality Check | Quarterly | Test for contamination; replace if necessary. |
By adhering to a consistent maintenance schedule and understanding the intricacies of the hydraulic system, operators can ensure the reliability and efficiency of their equipment, ultimately leading to improved productivity on job sites.
Parts Replacement for Efficiency
Ensuring optimal performance in machinery often hinges on the timely replacement of components. Regularly updating parts not only prolongs the lifespan of the equipment but also enhances its operational efficiency. Understanding which components require periodic replacement can lead to significant improvements in productivity and reliability.
Key Components for Replacement
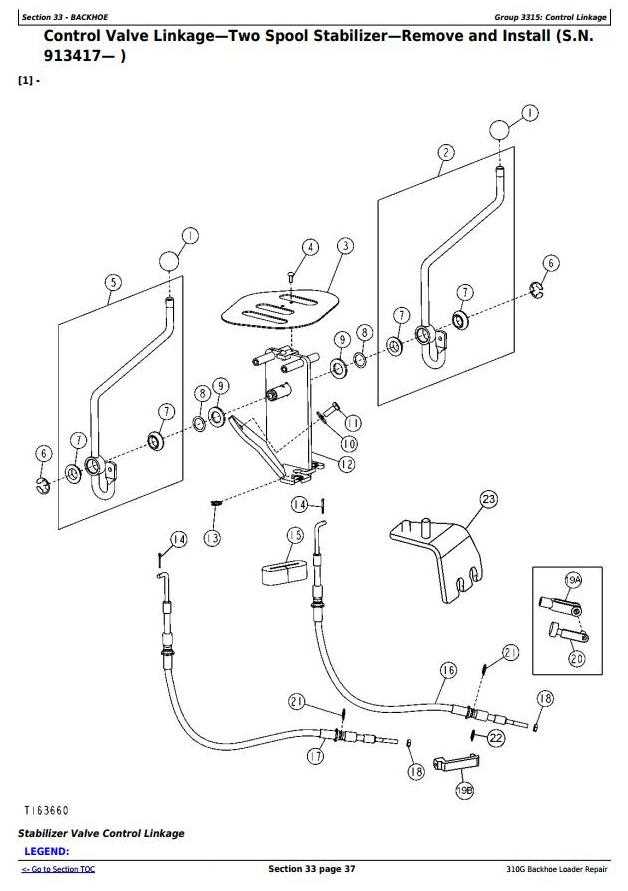
Focusing on certain critical elements can yield the best results. Here are some essential parts to consider:
- Filters: Regularly changing air, oil, and fuel filters prevents clogging and ensures smooth operation.
- Batteries: Replacing batteries at the first sign of decline can prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- Hydraulic Hoses: Inspecting and replacing worn hoses can avert leaks and pressure loss.
- Belts and Chains: These components wear over time and should be replaced to maintain efficiency.
Benefits of Timely Replacement
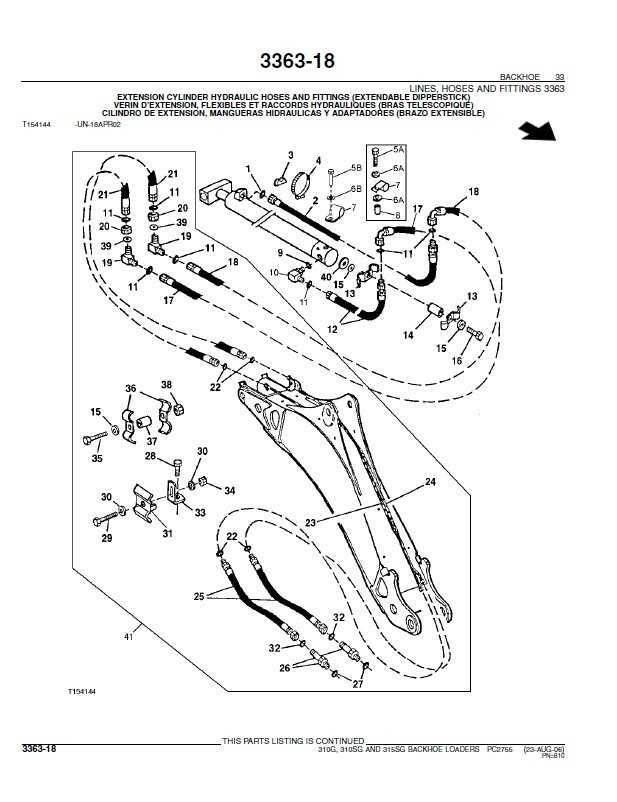
Investing time and resources into the replacement of parts offers numerous advantages:
- Improved Performance: Fresh components function better, providing enhanced power and responsiveness.
- Cost Savings: Preventive measures reduce the likelihood of costly repairs down the line.
- Safety: Maintaining equipment with new parts reduces the risk of accidents due to failure.
- Increased Productivity: Well-maintained machinery operates more efficiently, allowing for higher output.
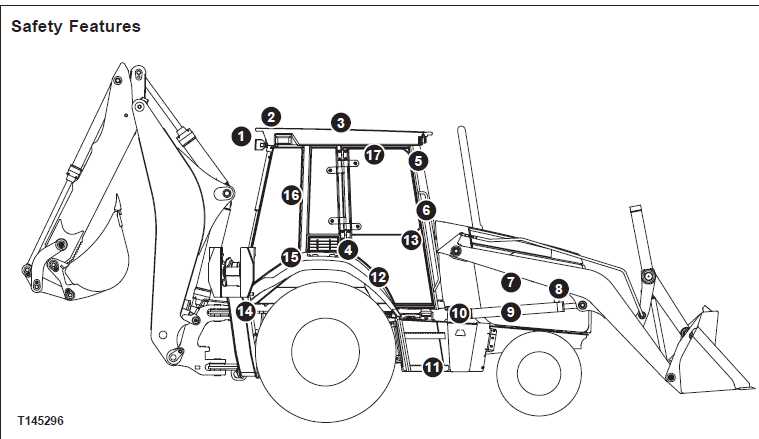
Safety Precautions During Repairs
When undertaking maintenance tasks on heavy machinery, ensuring a safe working environment is paramount. Proper precautions not only protect the individual performing the work but also safeguard the equipment and surrounding personnel. Adhering to established safety guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes safety glasses, gloves, hard hats, and steel-toed boots. Such gear helps mitigate the potential hazards associated with machinery handling and maintenance tasks.
Before starting any work, ensure that the machinery is powered down and secured against accidental activation. Use lockout/tagout procedures to prevent unexpected operation, which could lead to serious injury.
Familiarize yourself with the specific features and controls of the equipment you are working on. Understanding how the machinery functions will aid in identifying potential risks and contribute to safer handling during maintenance activities.
Maintain a clean and organized workspace. Clutter can lead to slips, trips, and falls, so keep tools and materials stored properly when not in use. Additionally, ensure that all spills are cleaned immediately to prevent accidents.
Regularly inspect tools and equipment before use to ensure they are in good condition. Damaged or worn tools can pose significant hazards and should be repaired or replaced promptly.
Finally, always work with a buddy when possible. Having another person nearby can provide assistance in case of an emergency and contributes to a safer working environment overall.
Where to Find Official Manuals

Accessing reliable documentation is essential for effective maintenance and operation of machinery. Official resources often provide the most accurate and comprehensive information, ensuring that users can perform tasks efficiently and safely.
Online Resources
- Manufacturer’s Website: Visit the official site where you can find a dedicated section for documentation.
- Authorized Dealers: Many dealers offer digital copies or can order printed versions directly for customers.
- Online Marketplaces: Check platforms that specialize in heavy equipment resources, as they may have official literature available for purchase.
Physical Locations

- Local Dealerships: Visit nearby dealerships that sell or service the equipment; they often have printed copies or can assist in obtaining them.
- Service Centers: Authorized service centers may have manuals on hand for reference or sale.