Comprehensive Guide to Briggs and Stratton Engine Repair
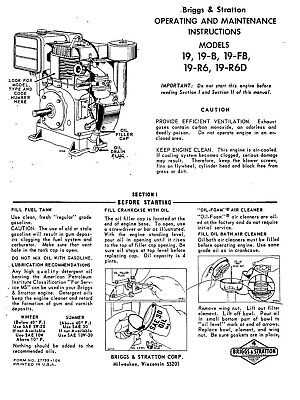
Understanding the intricacies of small motor upkeep is essential for enthusiasts and professionals alike. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the essential practices necessary for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of various machinery components. By following a systematic approach, users can ensure reliable operation and prevent potential failures.
Throughout this guide, readers will discover detailed procedures that encompass everything from basic troubleshooting to more complex adjustments. With the right knowledge and tools, individuals can confidently tackle common issues, enhancing the efficiency of their equipment. Each technique is designed to empower users, allowing them to take control of their maintenance routines.
Whether you are a seasoned technician or a novice, the insights provided here will prove invaluable. Emphasizing safety and efficiency, this resource aims to equip you with the skills necessary to keep your machinery running smoothly and effectively for years to come.

This section explores frequent problems encountered with small power units, providing insights into their origins and potential resolutions. Understanding these common challenges can help users maintain optimal performance and longevity.
Typical Problems
- Starting Difficulties
- Inefficient Fuel Consumption
- Unusual Noises
- Vibration Issues
- Overheating
Symptoms of Common Problems
- Failure to start
- Black smoke emissions
- Excessive vibration during operation
- Unresponsive throttle
- Leaking fluids
By recognizing these indicators, users can take appropriate actions to troubleshoot and mitigate issues effectively.
Essential Tools for Engine Repair
Having the right instruments is crucial for effectively restoring and maintaining small motors. This section highlights the vital implements that facilitate efficient diagnostics and fixes, ensuring that tasks are completed smoothly and successfully.
Basic Tools Required
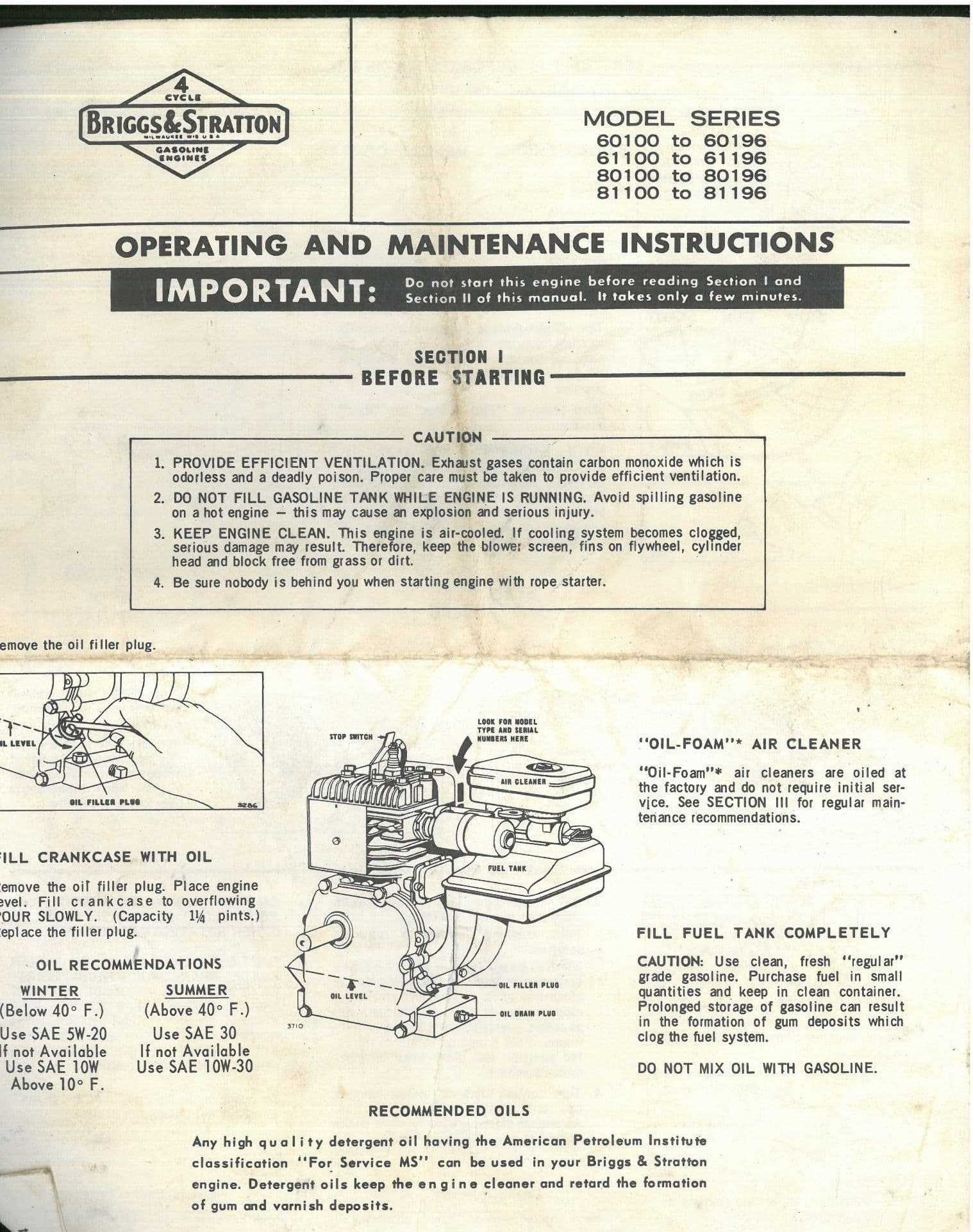
A comprehensive toolkit should include several foundational items that are indispensable for various tasks. These basic tools enable users to tackle common issues and perform regular maintenance with ease.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Socket Set | Used for loosening and tightening bolts |
| Screwdrivers | Essential for removing screws in various components |
| Wrenches | Helpful for gripping and turning nuts and bolts |
| Plier Set | Useful for gripping, bending, and cutting wire |
| Torque Wrench | Ensures proper tightening of fasteners |
Advanced Instruments
For more intricate tasks, specialized equipment is necessary. These advanced tools assist in diagnostics and complex repairs, enhancing precision and reliability during the maintenance process.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Compression Tester | Measures the compression pressure within cylinders |
| Multimeter | Tests electrical components and battery voltage |
| Fuel Pressure Gauge | Monitors fuel system pressure |
| Timing Light | Used for checking ignition timing |
| Leak Down Tester | Assesses the integrity of cylinder seals |
Step-by-Step Maintenance Procedures
This section outlines essential practices for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your machinery. Regular upkeep is vital to prevent issues and enhance functionality. Follow these procedures carefully for the best results.
Begin by gathering necessary tools and materials before starting the maintenance tasks. Ensure the area is clean and well-lit to facilitate easy access to the components involved.
Routine Tasks
| Task | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Check Oil Level | Inspect the oil level and add oil as needed to maintain proper lubrication. | Every 10 hours of use |
| Replace Air Filter | Remove the old filter and install a new one to ensure adequate airflow. | Every 25 hours of use |
| Inspect Spark Plug | Examine the spark plug for wear and replace it if necessary for efficient ignition. | Every 50 hours of use |
| Clean Fuel System | Flush the fuel lines and clean the carburetor to prevent clogging. | Annually |
By adhering to these outlined practices, you will ensure your machinery remains in top condition, ready for effective performance when needed. Consistent maintenance contributes to better efficiency and reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
Troubleshooting Starting Problems
Starting difficulties can arise from various issues, often requiring careful examination of several components. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective resolution. Below are common reasons for starting failures and steps to diagnose them.
- Fuel Issues:
- Check for adequate fuel in the tank.
- Inspect fuel lines for leaks or blockages.
- Ensure the fuel is fresh and not contaminated.
- Electrical Components:
- Examine the battery charge and connections.
- Test the ignition system for faults.
- Inspect wiring for damage or corrosion.
- Air Supply:
- Ensure the air filter is clean and unobstructed.
- Check for any intake blockages.
- Mechanical Parts:
- Look for signs of wear or damage in key components.
- Assess the starter mechanism for functionality.
By systematically examining these areas, you can often identify the underlying issue preventing successful starting. Proper maintenance and timely intervention can help avoid more significant problems in the future.
Understanding Engine Components and Functions

This section explores the essential parts of a motor and their respective roles. Each component contributes to the overall performance, efficiency, and reliability of the system. A thorough comprehension of these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Core Components
The primary parts include the cylinder, piston, and crankshaft. The cylinder houses the piston, which moves up and down, converting fuel into motion. The crankshaft translates this linear movement into rotational force, driving the entire mechanism.
Supporting Systems
In addition to core components, auxiliary systems such as the fuel delivery and ignition systems are vital. The fuel delivery system ensures the right mixture reaches the combustion chamber, while the ignition system sparks the fuel-air mixture, initiating the power cycle. Understanding these systems enhances troubleshooting efficiency.
How to Change Engine Oil
Regular maintenance of your power unit includes refreshing the lubricant to ensure optimal performance. Replacing the fluid helps maintain efficiency, prolongs the life of components, and minimizes wear.
Follow these steps for an effective oil change:
- Gather Necessary Tools:
- New lubricant
- Oil filter (if applicable)
- Drain pan
- Wrench
- Funnel
- Gloves
- Rags or paper towels
- Prepare the Area:
Ensure you are working in a well-ventilated area and have protection for the surface beneath. - Warm Up the Machine: Run the unit for a few minutes to thin the lubricant, making it easier to drain.
- Drain the Old Lubricant:
- Position the drain pan under the oil outlet.
- Remove the plug carefully and allow the fluid to fully drain.
- Replace the Oil Filter:
If your model has a filter, remove the old one and install the new one according to manufacturer instructions. - Add New Lubricant:
- Replace the drain plug securely.
- Using a funnel, pour in the new lubricant through the fill cap.
- Check the level with the dipstick, ensuring it is within the recommended range.
- Dispose of Old Fluid: Follow local regulations for proper disposal of the used lubricant.
Regularly changing the lubricant is a simple yet crucial task that keeps your machinery running smoothly and efficiently.
Replacing Spark Plugs Effectively

Changing the ignition components is essential for maintaining optimal performance in small machinery. Regularly replacing these vital parts ensures smooth operation and enhances the longevity of the equipment.
Tools Required
- Socket wrench set
- Torque wrench
- Gap gauge
- Anti-seize lubricant
Steps for Replacement
- Ensure the machinery is turned off and cooled down.
- Locate the ignition components and remove any protective covers.
- Use the socket wrench to unscrew the old components carefully.
- Inspect the removed parts for wear and carbon buildup.
- Set the gap on the new components using the gap gauge.
- Apply a small amount of anti-seize lubricant to the threads.
- Install the new components and tighten them to the manufacturer’s specifications using a torque wrench.
- Replace any covers and perform a final check before starting the equipment.
Following these steps will help ensure effective replacement and improve the performance of your machinery.
Cleaning the Air Filter

Maintaining a clean air intake component is essential for optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. A well-kept filter ensures that the machinery runs efficiently by allowing a proper airflow while preventing contaminants from entering the internal parts.
Importance of Regular Maintenance

Regularly inspecting and cleaning the air intake component can lead to several benefits:
- Improved airflow and performance
- Reduced fuel consumption
- Extended lifespan of internal components
- Minimized risk of damage from dirt and debris
Steps to Clean the Air Filter

- Locate the air intake component, usually secured with clips or screws.
- Carefully remove the filter from its housing.
- Gently tap the filter to dislodge dirt and debris.
- For thorough cleaning, rinse the filter with water or use compressed air.
- Allow the filter to dry completely before reinstalling.
- Reattach the filter securely in its housing, ensuring all clips or screws are fastened.
Following these steps will help maintain the efficiency and reliability of your equipment, ensuring smooth operation for years to come.
Fuel System Maintenance Tips

Proper upkeep of the fuel delivery system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention to this component ensures efficient operation and minimizes the risk of potential issues.
- Inspect Fuel Lines: Regularly check for cracks, leaks, or wear in the fuel lines. Replace any damaged sections to prevent fuel loss and maintain pressure.
- Clean Fuel Filter: Keep the fuel filter clean to ensure smooth flow. Replace it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or whenever performance decreases.
- Use Fresh Fuel: Always use fresh fuel to prevent gumming and varnishing, which can clog the system. Avoid using fuel that has been stored for extended periods.
- Check Fuel Tank: Ensure the fuel tank is clean and free from debris. Contaminants can hinder performance and damage the system.
- Monitor Fuel Quality: Regularly assess the quality of the fuel. Use additives if necessary to stabilize the fuel and keep the system clean.
By following these tips, you can significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of the fuel delivery system, ensuring smooth operation over time.
Diagnosing Overheating Issues

Identifying excessive heat problems in small machinery is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Overheating can lead to serious malfunctions if not addressed promptly. Understanding the symptoms and potential causes is the first step in effective troubleshooting.
One common indicator of overheating is unusual sounds or vibrations during operation. These can signify that components are not functioning harmoniously. Additionally, checking for visible signs of wear or damage, such as cracked casings or burnt components, can provide insights into the underlying issue.
Another essential factor to consider is the cooling system. Ensure that all airflow passages are clear and that cooling fans are operating correctly. Blockages or malfunctioning fans can hinder the cooling process, leading to elevated temperatures.
Inspecting fluid levels is equally important. Low or contaminated fluids can compromise cooling efficiency. Regular maintenance checks can help prevent overheating by ensuring that all fluids are at appropriate levels and in good condition.
Finally, understanding the operational environment can also play a significant role. Excessive heat may be exacerbated by external conditions, such as high ambient temperatures or inadequate ventilation. Adjusting the machinery’s location or adding protective barriers can mitigate these effects.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring a safe working environment is crucial when performing maintenance on machinery. Proper precautions can prevent accidents and injuries, allowing for a smooth process. Adhering to specific guidelines will help safeguard both the individual and the equipment.
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to harmful fumes.
- Disconnect the power source before starting any work to avoid accidental activation.
- Keep tools organized and within reach to reduce the risk of accidents.
Additionally, following a checklist can enhance safety:
- Inspect the workspace for any hazards such as spills or clutter.
- Ensure that all tools are in good condition and suitable for the task.
- Familiarize yourself with the machinery’s components and functions before beginning work.
- Have a first-aid kit readily available for emergencies.
By implementing these safety measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of incidents during maintenance tasks.
Seasonal Engine Preparation Checklist
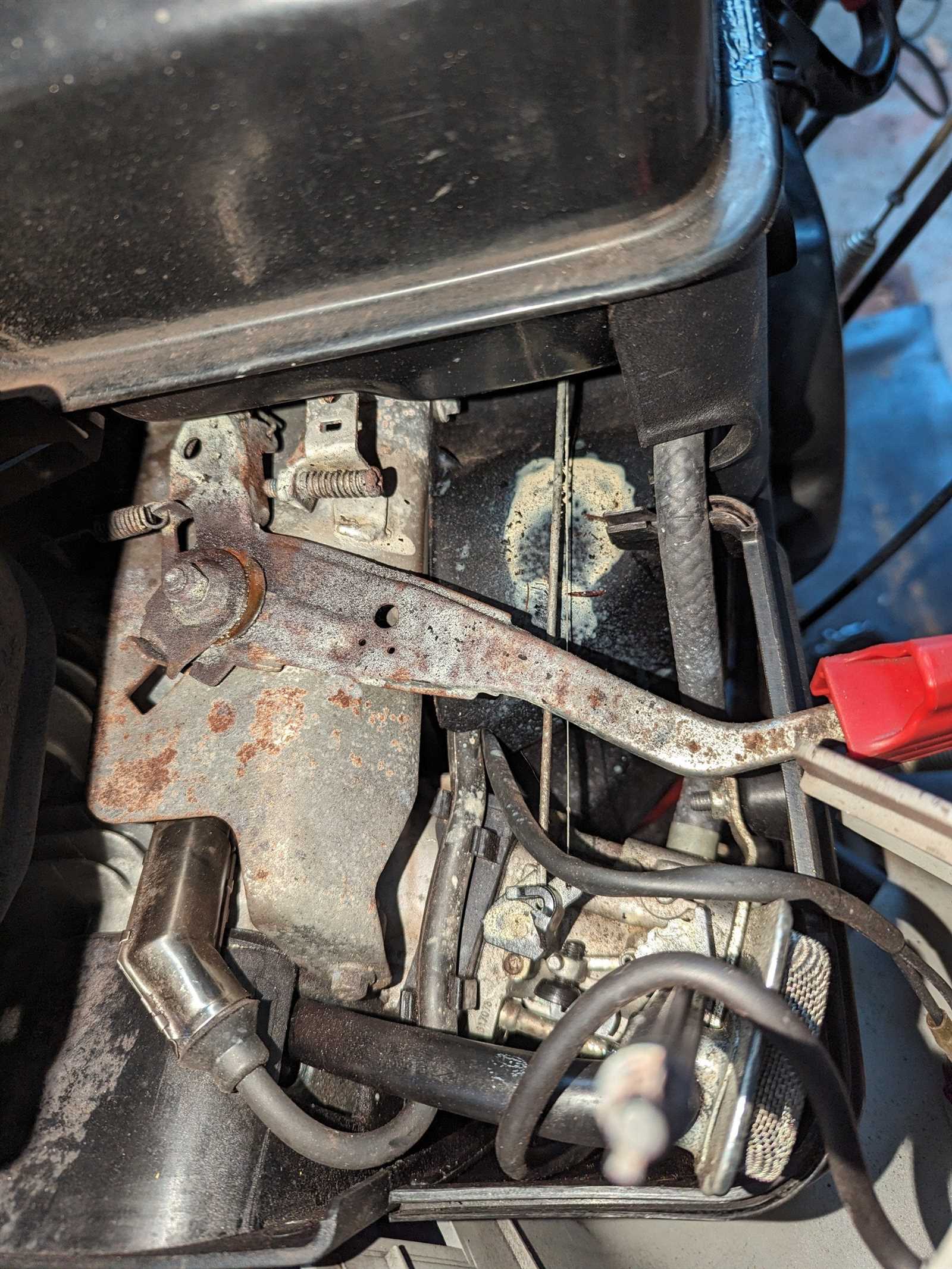

Proper maintenance of your machinery is essential for optimal performance throughout the year. As seasons change, specific tasks should be undertaken to ensure reliability and efficiency. This checklist outlines crucial steps to prepare your equipment for seasonal use.
1. Fuel System Maintenance: Begin by draining old fuel and replacing it with fresh fuel. Ensure that the fuel lines and filters are clear of debris to prevent blockages.
2. Air Filtration Inspection: Check and clean or replace the air filter. A clean filter promotes better airflow, enhancing performance and longevity.
3. Spark Plug Check: Inspect the spark plug for wear and deposits. Clean or replace it as necessary to guarantee proper ignition and efficient operation.
4. Lubrication: Examine all moving parts and apply suitable lubricant to reduce friction. This helps in maintaining smooth operation during usage.
5. Battery Care: If applicable, check the battery charge and clean the terminals. A well-maintained battery ensures reliable starting and power supply.
6. Safety Equipment Review: Confirm that all safety features are functional. This includes checking switches, guards, and emergency shut-off mechanisms to ensure user protection.
By following this checklist, you can enhance the performance and longevity of your machinery, making it ready for the tasks ahead.