Poclain Hydraulic Motor Repair Manual Guide

This section provides an in-depth exploration of techniques and best practices for maintaining complex machinery. It emphasizes the importance of understanding each component’s function and the systematic approach necessary for effective upkeep.
Proper care of these systems ensures longevity and optimal performance. A thorough comprehension of assembly and disassembly procedures can significantly reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
Additionally, this guide highlights common issues encountered during routine service. By familiarizing oneself with potential challenges, operators can adopt proactive measures, ensuring smooth functionality and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
Ultimately, this resource aims to empower users with the knowledge and skills required to execute maintenance tasks confidently, fostering a culture of excellence and reliability in equipment management.
Poclain Hydraulic Motor Overview

The device in question plays a crucial role in various industrial applications, converting fluid energy into mechanical power. Its design is engineered for efficiency and reliability, making it a preferred choice in demanding environments.
This particular apparatus features a compact structure, allowing for easy integration into diverse machinery. Its operational principles involve the precise control of fluid flow, which facilitates effective performance across a wide range of speeds and loads.
Additionally, the components are crafted from high-quality materials to ensure durability and longevity, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Understanding the fundamental aspects of this device is essential for optimizing its use in any project.
Common Issues in Poclain Motors
Understanding the typical problems encountered in these machinery units is crucial for effective maintenance and longevity. Operators often face various challenges that can lead to reduced efficiency or unexpected downtime. Identifying these issues early can prevent costly repairs and ensure optimal performance.
One prevalent issue involves leaks, which can arise from worn seals or damaged connections. Such leaks can significantly affect fluid levels and overall functionality. Another common concern is overheating, often linked to inadequate cooling systems or blocked vents. This can lead to decreased performance and potential failure if not addressed promptly.
Additionally, unusual noises during operation may indicate internal wear or misalignment of components. Regular inspection and timely adjustments can mitigate this problem. Lastly, contamination of the fluid can severely impact performance, making it essential to maintain clean operating conditions and change filters regularly.
Tools Needed for Repairs
Effective maintenance and troubleshooting require a selection of essential instruments and equipment. These tools facilitate accurate diagnostics, disassembly, and reassembly, ensuring optimal functionality of the machinery involved.
The following table outlines the key tools required for various tasks associated with the servicing of these systems:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrenches | To loosen and tighten bolts and fittings. |
| Screwdrivers | For removing and securing screws in different components. |
| Torque Wrench | To apply a specific torque to fasteners, preventing damage. |
| Pliers | For gripping and bending wire or small components. |
| Multimeter | For electrical diagnostics and testing connections. |
| Oil Filter Wrench | To remove and install oil filters easily. |
| Cleaning Supplies | For maintaining cleanliness during the servicing process. |
Having the right tools at hand not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to the longevity and performance of the equipment. Investing in quality instruments is essential for successful outcomes in these tasks.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
The disassembly of complex machinery is a crucial procedure that requires careful attention and systematic steps. This section outlines the necessary actions to safely dismantle the unit, ensuring that all components are properly handled and cataloged for reassembly.
1. Preparation: Before beginning the disassembly, gather all essential tools and safety equipment. Ensure the workspace is clean and organized to facilitate an efficient process.
2. Documentation: Take photographs or make detailed notes of the assembly configuration. This visual reference will aid in the reassembly phase, helping to recall the placement of each component.
3. Initial Inspection: Examine the exterior for any signs of damage or wear. Identifying these issues early can prevent complications during disassembly.
4. Component Removal: Begin by carefully removing any external attachments, such as covers or protective casings. Use appropriate tools to avoid damaging the parts.
5. Sequential Disassembly: Follow a logical sequence when removing internal components. Start from the outermost parts and work inward. Label each piece and store them in a designated container to keep everything organized.
6. Final Assembly Inspection: Once disassembled, conduct a thorough inspection of all components. Look for signs of wear or damage that may require attention during reassembly.
By adhering to these steps, the disassembly process can be executed smoothly, laying the groundwork for effective maintenance and reassembly of the unit.
Inspecting Internal Components
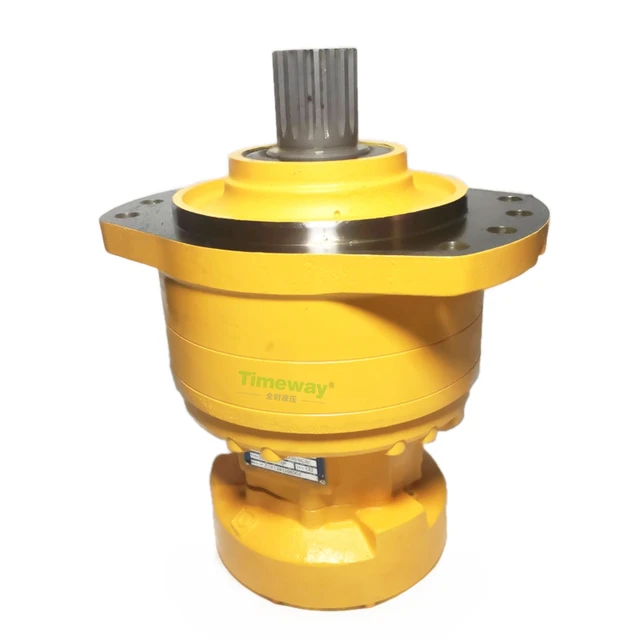

Regular examination of the internal elements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the machinery. This process involves a thorough assessment of various parts to identify any signs of wear, damage, or potential failure. A proactive approach to inspection can prevent costly breakdowns and maintain operational efficiency.
Tools and Preparation

Before starting the inspection, gather the necessary tools, including a torque wrench, measuring gauges, and cleaning supplies. Ensure that the workspace is organized and free from debris to facilitate a smooth inspection process. Proper lighting is also essential to identify subtle defects that may not be easily visible in poor conditions.
Step-by-Step Inspection Process

Begin the evaluation by disassembling the unit, taking care to document each step for reassembly. Inspect critical components such as seals, bearings, and gears for signs of degradation. Pay special attention to areas where friction occurs, as these are often the first to show wear. Replace any damaged parts and clean all surfaces to eliminate contaminants that could affect performance.
Repairing Hydraulic Seals
Seals play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of fluid systems by preventing leaks and ensuring optimal performance. Proper attention to these components can greatly enhance the efficiency and longevity of your machinery. This section will delve into techniques for addressing common issues related to seal integrity.
Common Issues with Seals
- Wear and Tear: Over time, seals can become worn due to friction and exposure to various elements.
- Contamination: Foreign particles can compromise the seal’s ability to function effectively.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect fitting can lead to premature failure.
Steps for Maintenance
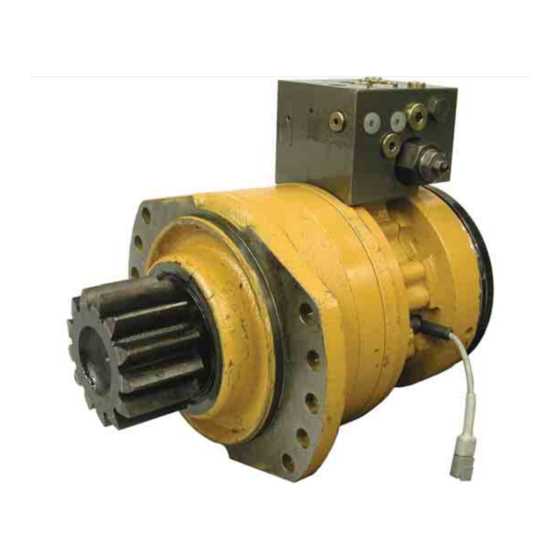

- Inspection: Regularly check seals for signs of damage, such as cracks or deformation.
- Cleaning: Remove contaminants carefully to avoid further damage.
- Replacement: If wear is significant, consider replacing the seal with a compatible alternative.
- Proper Installation: Follow guidelines to ensure correct fitting, utilizing appropriate tools.
By following these steps, you can effectively manage the condition of seals, thereby improving overall system functionality and reducing the likelihood of leaks.
Reassembling the Hydraulic Motor
This section provides a comprehensive guide to the process of putting together a fluid transfer device after disassembly. Proper reassembly is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the unit. Follow the outlined steps carefully to avoid any potential issues.
Preparation for Assembly
Before beginning the reassembly process, ensure that all components are clean and free from any debris. Inspect each part for wear or damage, replacing any components as necessary. Gather the required tools and materials, including lubricants and seals, to facilitate a smooth assembly.
Step-by-Step Assembly Process
Start by aligning the main casing components. Apply a thin layer of lubricant to the seals before placing them in their designated grooves. Carefully insert the inner components, ensuring they fit securely without forcing them. Gradually tighten the fasteners according to the manufacturer’s specifications to maintain uniform pressure throughout the assembly. Finally, conduct a thorough inspection to verify that everything is properly aligned and secured.
Following these steps will help ensure that the unit functions correctly and efficiently after reassembly.
Testing Functionality After Repair
Once maintenance has been completed, it’s essential to verify that the equipment operates correctly and meets performance standards. This stage is crucial for ensuring that all components function as intended and that no issues remain unaddressed. Proper assessment can prevent future complications and ensure reliability in operation.
To effectively test the unit, follow these steps:
| Step | Description | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inspect all connections and ensure they are secure. | No leaks or loose fittings. |
| 2 | Run the system at low pressure to check for irregularities. | Stable operation without unusual sounds. |
| 3 | Gradually increase pressure while monitoring performance. | Consistent output and smooth operation. |
| 4 | Check for any abnormal vibrations or heating. | Normal temperature and minimal vibrations. |
| 5 | Conduct a final operational test under full load. | Performance meets specified criteria. |
Completing these tests ensures the functionality of the system and helps maintain high operational efficiency. Regular assessment after servicing can extend the lifespan of the equipment and enhance its reliability in the field.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring the extended lifespan of your machinery. Regular attention and care can prevent costly breakdowns and enhance performance. Here are some valuable strategies to keep your equipment running smoothly over time.
Regular Inspections
- Conduct frequent visual checks for signs of wear or damage.
- Monitor fluid levels and ensure they are within recommended ranges.
- Examine hoses and connections for leaks or deterioration.
Fluid Management
- Change oils and fluids at recommended intervals to prevent contamination.
- Use high-quality lubricants that meet manufacturer specifications.
- Ensure proper filtration to keep fluids clean and effective.
By implementing these practices, you can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of your equipment, reducing the likelihood of unexpected issues and downtime.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
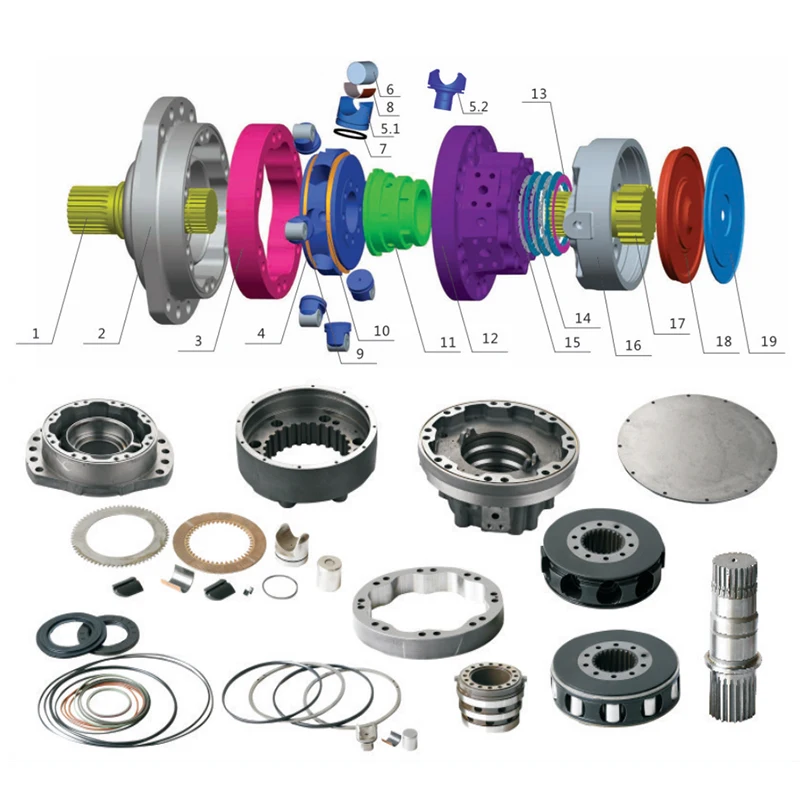

This section addresses frequent issues encountered in performance systems and provides guidance for effective diagnosis and resolution. Understanding the symptoms can significantly enhance the efficiency of the troubleshooting process.
Identifying Symptoms

- Unusual noise during operation
- Inconsistent output or power loss
- Excessive heat generation
- Fluid leakage
Steps for Diagnosis
- Inspect for external damage or loose connections.
- Check fluid levels and quality.
- Listen for irregular sounds that may indicate wear or internal issues.
- Monitor temperature variations during operation.
By following these guidelines, operators can systematically address common issues and restore optimal functionality.
Recommended Replacement Parts
When maintaining complex machinery, selecting the right components for substitution is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Using high-quality replacement items not only enhances functionality but also minimizes the risk of future issues.
Essential Components
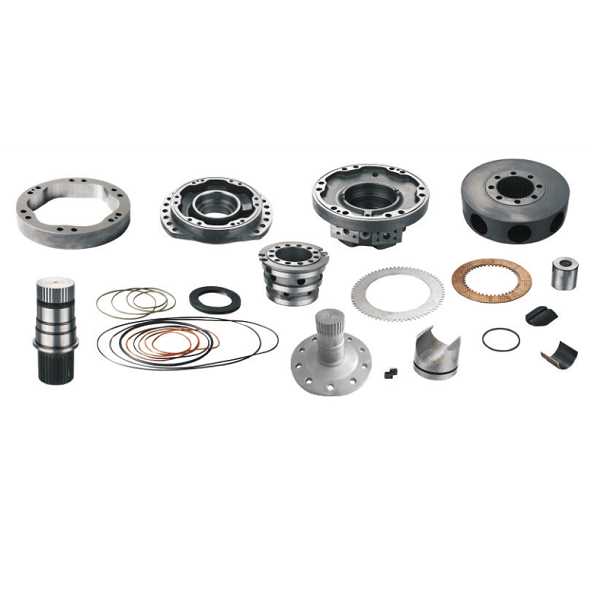

Among the vital parts to consider for replacement are seals, bearings, and pistons. These elements play a significant role in maintaining efficiency and preventing leaks. Ensuring that they meet or exceed original specifications is essential for reliable operation.
Quality Assurance
Opting for components from reputable manufacturers guarantees durability and performance. It’s advisable to verify compatibility and standards to avoid potential complications during installation and use.
When to Consult a Professional
Determining the right moment to seek expert assistance can significantly impact the efficiency and longevity of your equipment. While some issues may seem manageable, others require specialized knowledge and experience to ensure proper handling and resolution. Understanding the signs that indicate a need for professional intervention is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Signs Indicating Professional Help is Needed
Be attentive to the following indicators that suggest it may be time to consult an expert:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Unusual Noises | Any strange sounds during operation that were not previously present can signal underlying issues. |
| Performance Decline | A noticeable decrease in functionality or output often indicates a need for a thorough inspection. |
| Frequent Breakdowns | Recurrent failures or malfunctions may suggest more complex problems that require specialized diagnosis. |
| Fluid Leaks | Visible leaks can not only impact performance but also pose safety risks and environmental concerns. |
Benefits of Professional Consultation
Engaging with a specialist ensures that your equipment receives the necessary attention and expertise. Professionals can accurately diagnose problems, recommend effective solutions, and provide maintenance tips that extend the lifespan of your machinery. Ultimately, this approach minimizes downtime and promotes efficient operation.