Comprehensive Repair Manual for the 2007 Dodge Caliber

This section provides a detailed overview for individuals seeking to enhance their understanding of automotive upkeep and troubleshooting. Aiming to empower car owners, it outlines essential practices for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of their vehicles.
From routine checks to more complex procedures, this guide serves as a valuable resource for both novice and experienced mechanics. The emphasis is placed on clarity and accessibility, enabling readers to navigate through various topics with ease and confidence.
As you delve into the specifics, you will discover practical insights and valuable tips designed to assist in addressing common issues. Engaging with this material will equip you with the knowledge necessary to maintain your vehicle effectively, ensuring it remains in excellent condition for years to come.
Dodge Caliber 2007 Repair Manual
This section provides essential guidance for maintaining and troubleshooting a compact vehicle model that emerged in the late 2000s. It covers a range of procedures and techniques that owners and technicians can use to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the automobile.
Key Maintenance Practices
Regular upkeep is vital for any automobile. The following practices are recommended to keep the vehicle in top condition:
- Routine oil changes and fluid checks
- Inspection of brakes and tires
- Monitoring of electrical systems and battery health
Common Issues and Solutions
Owners may encounter various challenges. Below are some prevalent concerns along with potential resolutions:
| Issue | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Overheating | Temperature gauge rising, steam from hood | Check coolant levels, inspect radiator for leaks |
| Electrical Failure | Dashboard lights flickering, starting issues | Inspect battery connections, replace faulty fuses |
| Transmission Slippage | Delayed shifting, unusual noises | Check transmission fluid levels, consult a specialist if necessary |
Engine Specifications and Maintenance
This section provides an overview of the vital aspects concerning the power unit of the vehicle, emphasizing the significance of regular upkeep and understanding the technical details for optimal performance.
Key specifications include:
- Engine Type: Inline 4-cylinder
- Displacement: 2.0 liters
- Horsepower: Approximately 158 hp
- Torque: About 141 lb-ft
- Fuel Type: Unleaded gasoline
Maintenance recommendations consist of:
- Regular oil changes every 5,000 miles or as indicated by the oil life monitor.
- Checking and replacing air filters to ensure proper airflow.
- Monitoring coolant levels and replacing as necessary to prevent overheating.
- Inspecting belts and hoses for signs of wear or damage.
- Scheduling periodic inspections for engine diagnostics to catch potential issues early.
Transmission and Drivetrain Overview
The transmission and drivetrain system is crucial for the efficient performance of any vehicle, facilitating the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding the components involved in this system helps in diagnosing issues and performing necessary maintenance.
Key Components
This system consists of several integral parts, including the gearbox, drive shafts, and differentials. The gearbox is responsible for altering the gear ratios, allowing the vehicle to operate at various speeds while maintaining optimal engine performance. Drive shafts transmit torque to the wheels, while differentials enable smooth turning by allowing wheels to rotate at different speeds.
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspections of the transmission fluid level and condition are essential for preventing potential failures. A well-maintained system ensures longevity and reliable performance. Additionally, any unusual noises or shifting problems should be addressed promptly to avoid further damage.
Electrical System Troubleshooting
This section focuses on diagnosing and resolving issues within the electrical system of a compact vehicle. Effective troubleshooting involves a systematic approach to identify malfunctions and restore proper functionality. Understanding the components and their interactions is crucial for efficient repairs.
Common Symptoms of Electrical Issues
- Dim or flickering lights
- Unresponsive electrical accessories
- Frequent blown fuses
- Battery not holding a charge
- Starter motor failure
Troubleshooting Steps
- Inspect the battery and connections for corrosion or loose terminals.
- Check the fuses for any that are blown and replace them as necessary.
- Test the alternator output to ensure it is charging the battery properly.
- Examine wiring harnesses for damage, fraying, or shorts.
- Utilize a multimeter to diagnose voltage and continuity in circuits.
Suspension and Steering Insights
The interplay of suspension and steering systems plays a crucial role in vehicle handling and comfort. Understanding these components can significantly enhance driving experience and safety. Proper alignment, quality shocks, and responsive steering are essential for maintaining control on various terrains.
Components like struts and springs absorb road imperfections, ensuring a smooth ride. Additionally, the steering mechanism allows precise maneuvering, which is vital for navigating tight corners and maintaining stability. Regular inspection and maintenance of these systems are recommended to prevent potential issues and ensure longevity.
Brake System Inspection Procedures
This section outlines the essential steps for assessing the braking system’s performance and integrity. Regular evaluations help ensure safety and responsiveness during operation, minimizing risks associated with brake failures.
Visual Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual assessment of the brake components. Look for signs of wear, leaks, or corrosion. Pay attention to the condition of brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels.
| Component | Inspection Points | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Brake Pads | Thickness, cracking, and uneven wear | Replace if less than 3mm thick |
| Rotors | Scoring, warping, and surface condition | Resurface or replace if damaged |
| Brake Fluid | Color, level, and moisture content | Flush and replace if dirty or contaminated |
Functional Testing
Conduct a functional test to evaluate the effectiveness of the braking system. Check the pedal feel and responsiveness during gradual and sudden braking.
Cooling System Components Explained
The cooling system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating. This system comprises various components, each serving a specific function to ensure the engine runs efficiently and reliably.
Radiator
The radiator is essential for dissipating heat from the coolant. As the engine operates, the coolant absorbs heat and flows into the radiator, where it cools down by transferring heat to the surrounding air. This process is vital for maintaining the engine’s temperature within the designated range.
Water Pump
The water pump circulates coolant throughout the cooling system. It ensures that coolant flows from the engine to the radiator and back again, facilitating continuous heat exchange. A malfunctioning water pump can lead to inadequate cooling, resulting in potential engine damage.
Understanding these components is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting of the cooling system, ensuring long-lasting engine performance.
Body and Interior Repair Guidelines
This section provides essential advice for addressing issues related to the exterior and interior of your vehicle. Proper maintenance and repair can enhance both aesthetics and functionality, ensuring a comfortable driving experience.
Begin with a thorough inspection to identify any dents, scratches, or damages that may affect the vehicle’s appearance. For minor surface imperfections, consider using polishing compounds or touch-up paint. In cases of significant bodywork, consult professional services to guarantee a high-quality finish.
Interior components, such as upholstery and trim, require special attention to maintain their condition. Use appropriate cleaners and conditioners to keep materials in optimal shape. If you encounter tears or significant wear, explore options for patching or replacing affected areas.
When dealing with electronic elements like windows and locks, ensure all connections are secure. Faulty wiring can lead to malfunctions, so regular checks are recommended. Additionally, keep an eye on weather stripping to prevent water intrusion and maintain insulation.
Regular upkeep of both exterior and interior will contribute to the longevity of your vehicle. Addressing issues promptly can prevent further damage and preserve the overall value of your investment.
Safety Features and Adjustments
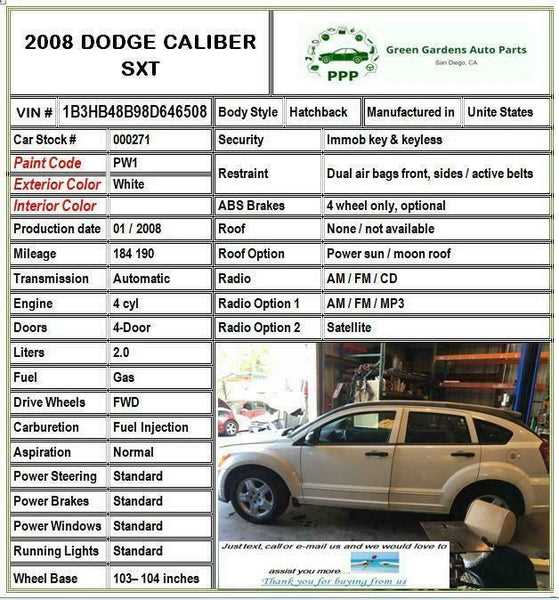
Ensuring the protection of passengers is paramount in any vehicle design. This section focuses on the integral safety components and necessary modifications that enhance the overall security and comfort during operation. By understanding these elements, users can ensure that their vehicle maintains optimal safety standards.
Key Safety Components
Modern vehicles are equipped with various safety mechanisms, including advanced airbag systems, electronic stability control, and anti-lock braking systems. These features work in tandem to minimize the risk of accidents and provide protection in the event of a collision. Regular assessments of these systems are essential to confirm their functionality and reliability.
Adjustment Procedures
To maintain effective safety features, periodic adjustments are required. Alignment checks for the suspension system, calibration of sensors for safety aids, and routine inspections of braking components are critical tasks. Proper adjustments ensure that all safety mechanisms operate correctly, providing peace of mind for drivers and passengers alike.
Common Issues and Solutions
This section addresses frequent challenges faced by vehicle owners and provides effective resolutions to enhance overall performance and reliability. Understanding these common complications can lead to improved maintenance and longer vehicle lifespan.
Electrical System Problems
One of the primary concerns involves the electrical system. Issues such as dimming lights or unresponsive components can arise from faulty wiring or a weak battery. Solution: Regularly check connections and replace worn-out batteries to ensure a stable electrical supply.
Transmission Concerns
Another typical issue relates to transmission performance. Drivers may experience slipping gears or delayed engagement, which can stem from low fluid levels or a failing transmission. Solution: Maintain proper fluid levels and consider a professional inspection if problems persist.
Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
Effective troubleshooting requires a variety of specialized instruments and devices that aid in identifying and resolving issues within a vehicle’s systems. These tools are essential for accurate assessments and can significantly enhance the efficiency of repair tasks.
Essential Diagnostic Instruments
- OBD-II Scanner: This device connects to the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic port, retrieving error codes and real-time data to assist in diagnosing faults.
- Multimeter: Useful for measuring voltage, current, and resistance, a multimeter helps evaluate electrical systems and components.
- Scan Tool: A more advanced version of an OBD-II scanner, this tool provides in-depth diagnostics and can perform bi-directional tests on certain systems.
Supporting Equipment
- Compression Tester: This instrument measures the compression in each cylinder, providing insight into engine health.
- Fuel Pressure Gauge: Used to assess the fuel delivery system, ensuring adequate pressure for optimal engine performance.
- Vacuum Gauge: This tool helps diagnose issues related to air intake and exhaust systems by measuring the vacuum in the intake manifold.
Utilizing the right diagnostic equipment is crucial for achieving accurate results and ensuring effective maintenance. Familiarity with these tools can lead to more efficient troubleshooting and successful repairs.
Recommended Service Intervals

Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle. Adhering to suggested service schedules helps identify potential issues before they escalate, maintaining the overall reliability and safety of the automobile.
General Maintenance Schedule
The following intervals are commonly recommended for various services:
- Oil Change: Every 5,000 to 7,500 miles
- Fluid Checks: Every 3,000 miles
- Tire Rotation: Every 6,000 to 8,000 miles
- Brake Inspection: Every 10,000 miles
- Battery Check: Annually
Additional Services
In addition to standard checks, consider the following at specific intervals:
- Air Filter Replacement: Every 15,000 to 30,000 miles
- Spark Plug Replacement: Every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on type
- Transmission Fluid Change: Every 30,000 to 60,000 miles
- Timing Belt Replacement: Generally around 60,000 to 100,000 miles
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for precise intervals and specific recommendations tailored to your vehicle model.