Comprehensive Guide to Repairing the 2005 Hyundai Elantra

Maintaining an automobile in optimal condition requires a systematic approach to understanding its components and systems. This section aims to provide essential insights into the intricacies of a specific model’s upkeep, focusing on common challenges and effective solutions.
Whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or a newcomer to vehicle care, possessing detailed information is crucial for successful handling of various situations. By equipping yourself with knowledge about procedures and specifications, you can ensure that your vehicle remains reliable and efficient throughout its lifespan.
From minor adjustments to significant repairs, the information presented here will empower you to take informed actions. Emphasizing clarity and accessibility, this guide serves as a valuable resource for anyone looking to enhance their understanding and skills in automotive care.
Understanding the 2005 Hyundai Elantra
This section aims to provide insights into a specific compact vehicle, focusing on its features, functionality, and maintenance considerations. Emphasizing essential components and systems will help owners and enthusiasts appreciate its design and performance.
Equipped with a variety of technological advancements, this model offers a balance of efficiency and comfort. Its architecture supports a range of driving needs, making it suitable for both city and highway environments.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine | 4-cylinder engine providing reliable performance and fuel efficiency. |
| Transmission | Available in manual and automatic options, enhancing driving flexibility. |
| Interior | Spacious cabin with user-friendly controls and ample storage. |
| Safety | Equipped with advanced safety features to ensure passenger protection. |
Understanding the intricacies of this vehicle enables better decision-making regarding maintenance and upgrades, ultimately enhancing the driving experience.
Engine Specifications and Features
This section delves into the essential characteristics and capabilities of the powertrain, emphasizing performance, efficiency, and design. Understanding these elements is crucial for both enthusiasts and technicians alike, as they provide insight into the vehicle’s operational dynamics.
Performance Metrics
The heart of any automobile is its engine, and several key metrics define its capabilities. These specifications influence everything from acceleration to fuel consumption.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Configuration | Inline 4 |
| Displacement | 2.0 liters |
| Horsepower | 138 hp |
| Torque | 136 lb-ft |
| Fuel Type | Regular Unleaded |
| Compression Ratio | 10.5:1 |
Design Features
The construction and technological advancements of the engine contribute significantly to its overall functionality. Various design elements enhance both efficiency and durability, ensuring a reliable performance over time.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

Understanding the typical problems that may arise in vehicles can significantly aid in maintenance and repair efforts. This section aims to highlight frequent challenges encountered by drivers, along with practical solutions to address them effectively.
Engine Performance Problems
One of the most prevalent concerns involves engine performance. Symptoms such as stalling, rough idling, or difficulty starting can indicate underlying issues. Regular inspections of fuel filters, spark plugs, and air intake systems are crucial for maintaining optimal engine efficiency. Checking for error codes using a diagnostic tool can provide insights into specific malfunctions.
Electrical System Failures
Another common area of concern is the electrical system. Drivers may experience problems such as dimming headlights or non-functioning accessories. These issues often stem from a failing battery or corroded connections. Routine checks of the battery condition and cleaning of electrical terminals can prevent many electrical faults. Additionally, ensuring all fuses are intact is essential for a properly functioning system.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Guidelines

Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle. Following a structured approach can help prevent potential issues and maintain its reliability. This section outlines a series of fundamental practices that every vehicle owner should consider.
-
Check Fluid Levels:
- Engine oil
- Coolant
- Brake fluid
- Transmission fluid
- Windshield washer fluid
Inspect these fluids regularly and top them off as needed to ensure smooth operation.
-
Inspect Filters:
- Air filter
- Cabin air filter
- Fuel filter
Replace filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to maintain air quality and engine efficiency.
-
Tire Maintenance:
- Check tire pressure monthly
- Inspect tread depth
- Rotate tires every 5,000 to 7,500 miles
Proper tire care enhances fuel efficiency and ensures safety on the road.
-
Brake System Inspection:
- Check brake pads and rotors for wear
- Inspect brake lines for leaks
Regular checks of the braking system are crucial for safety and performance.
-
Battery Care:
- Clean battery terminals
- Check for corrosion
- Test battery charge
Maintaining the battery can prevent unexpected breakdowns and prolong its lifespan.
By adhering to these maintenance steps, vehicle owners can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of their automobiles, ultimately ensuring a safer driving experience.
Fluid Types and Replacement Intervals
Maintaining the various liquids in your vehicle is essential for its optimal performance and longevity. Different fluids serve specific purposes, ranging from lubrication to cooling and hydraulic functions. Regular monitoring and timely replacement of these substances can prevent mechanical issues and enhance overall efficiency.
Engine Oil: This lubricant is crucial for reducing friction between moving parts. It’s recommended to replace it every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, depending on driving conditions. Using the right viscosity is vital for effective operation.
Transmission Fluid: Essential for smooth gear shifts, this fluid should be checked regularly. A typical replacement interval is every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, although severe driving conditions may necessitate more frequent changes.
Coolant: This fluid prevents overheating and protects the engine from corrosion. It is advisable to replace it every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, or as specified in the guidelines.
Brake Fluid: Critical for safety, this fluid should be inspected at least once a year, with a replacement interval of every 2 years to ensure responsive braking performance.
Power Steering Fluid: This fluid aids in steering ease. Typically, it requires replacement every 50,000 miles, although you should always check the level regularly.
By adhering to these replacement schedules, you can help ensure that your vehicle operates smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
Brake System Overview and Care

The braking mechanism is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring safe operation by allowing the driver to reduce speed or come to a complete stop. Understanding its functionality and maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
This system typically comprises various elements such as pads, rotors, and calipers, which work in tandem to create friction. Regular inspection of these components is vital, as wear and tear can significantly affect efficiency and safety.
To maintain the braking system, it is important to check the brake fluid level, inspect pads for thickness, and listen for unusual noises during operation. Any signs of decreased performance should prompt immediate attention to prevent potential hazards.
Routine maintenance practices, including replacing worn components and flushing brake fluid, can enhance reliability and ensure the vehicle responds effectively under various conditions. Prioritizing this aspect of vehicle care contributes to overall safety on the road.
Electrical System Components Explained

The electrical system in a vehicle is crucial for its operation, encompassing various elements that work in harmony to ensure functionality and safety. This intricate network is responsible for powering accessories, starting the engine, and controlling critical systems. Understanding the components of this network is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Main Components

Several key elements comprise the electrical system, each serving a unique purpose. Here are the primary components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy and supplies power to start the engine and operate electrical devices. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity while the engine is running, replenishing the battery and powering the electrical systems. |
| Starter Motor | Engages the engine to initiate combustion, allowing the vehicle to start. |
| Fuses | Protect circuits by preventing excessive current flow, thereby avoiding damage to components. |
| Wiring Harness | Connects various electrical components, facilitating communication and power distribution throughout the vehicle. |
Importance of Regular Checks
Regular inspections of the electrical system components can help prevent malfunctions and enhance the overall performance of the vehicle. Identifying and addressing issues promptly can lead to a safer and more reliable driving experience.
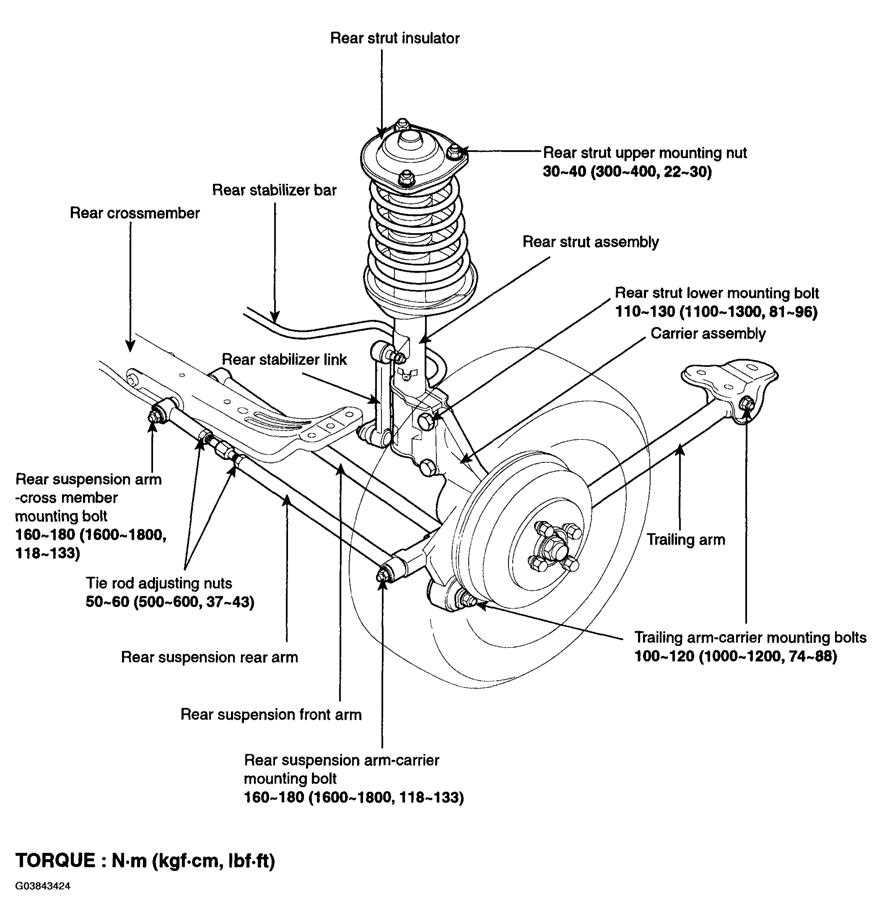
Suspension and Steering Maintenance Tips
Proper upkeep of the suspension and steering systems is essential for ensuring optimal vehicle performance and safety. Regular attention to these components can enhance ride quality, improve handling, and extend the lifespan of critical parts.
1. Routine Inspections: Frequently examine the suspension and steering elements for signs of wear, such as leaks, cracks, or unusual noises. Addressing issues early can prevent more significant problems down the line.
2. Alignment Checks: Ensure that wheel alignment is checked periodically. Misalignment can lead to uneven tire wear and affect handling, making it crucial to keep everything aligned correctly.
3. Fluid Levels: Maintain appropriate levels of power steering fluid and inspect for leaks. Regularly topping off fluids helps keep the steering system operating smoothly and effectively.
4. Tire Maintenance: Regularly inspect and rotate tires to promote even wear. Proper tire pressure is also vital for optimal performance and safety.
5. Component Replacement: Pay attention to the condition of bushings, struts, and shocks. Replacing worn components can greatly enhance comfort and stability while driving.
6. Professional Servicing: Consult a qualified technician for in-depth maintenance and repairs. Professionals can provide insights and services that ensure all systems are functioning at their best.
Body and Interior Repair Techniques
This section explores essential methods for restoring vehicle exteriors and interiors, focusing on enhancing aesthetics and functionality. Understanding these techniques can significantly improve the overall condition of the automobile, ensuring both visual appeal and comfort for occupants.
Key methods for addressing bodywork include:
- Surface Preparation: Cleaning and sanding surfaces to ensure proper adhesion of paints and coatings.
- Filling and Smoothing: Using fillers to repair dents and imperfections before applying a finish.
- Painting: Techniques for applying paint evenly, including the use of primers and clear coats for durability.
Interior restoration techniques focus on enhancing comfort and appearance:
- Upholstery Repair: Methods for fixing or replacing fabric and leather materials to restore seating quality.
- Dashboard Restoration: Techniques for repairing cracks and fading in dashboard surfaces to improve aesthetics.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Best practices for keeping interior surfaces clean and well-maintained, including recommended cleaning products.
Employing these techniques not only rejuvenates the vehicle’s appearance but also contributes to a more enjoyable driving experience.
Wheel Alignment and Tire Care
Proper adjustment of wheels and maintenance of tires are crucial for optimal vehicle performance. Ensuring that the wheels are aligned correctly can significantly enhance handling, fuel efficiency, and overall safety. Additionally, regular attention to tire condition can extend their lifespan and improve ride comfort.
Alignment involves the adjustment of the angles of the wheels, ensuring they are perpendicular to the ground and parallel to each other. Misalignment can occur due to various factors, such as hitting potholes or curbs, leading to uneven tire wear and compromised steering response. Regular checks are recommended to maintain precision and prevent costly replacements.
Tire care includes monitoring tire pressure, tread depth, and overall condition. Maintaining the correct inflation level is essential for both safety and efficiency. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased wear and reduced fuel economy, while over-inflation may cause a harsh ride and decreased traction. Periodic inspections for any signs of damage or irregular wear are also vital to ensure that tires perform effectively.
Incorporating a routine for wheel alignment and tire maintenance will not only enhance driving experience but also contribute to the longevity of your vehicle’s components. By paying attention to these aspects, you can ensure a safer and smoother journey.
Cooling System Functions and Maintenance
The cooling system is essential for regulating the engine’s temperature, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating. It plays a crucial role in dissipating heat generated during combustion, maintaining a safe operating environment for various engine components.
Regular maintenance of this system is vital to ensure its efficiency and longevity. Checking coolant levels, inspecting hoses for leaks, and ensuring the radiator is free of debris are all key tasks. Additionally, periodic flushing of the cooling system can help remove buildup and contaminants that could impair function.
Monitoring the temperature gauge on the dashboard is also important. If the engine temperature exceeds the normal range, it may indicate a problem within the cooling system that needs immediate attention. Maintaining the integrity of this system not only enhances engine performance but also contributes to overall vehicle reliability.
Transmission Types and Maintenance Needs
Understanding the various types of gear-shifting mechanisms in vehicles is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Each system has unique characteristics that dictate specific care requirements. Proper maintenance not only enhances efficiency but also prolongs the lifespan of these critical components.
Types of Transmission Systems
- Automatic Transmission: This system shifts gears automatically based on speed and load, providing ease of use.
- Manual Transmission: In this system, the driver manually shifts gears, offering more control and engagement.
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT): A type of automatic transmission that provides seamless acceleration without distinct gear shifts.
- Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT): Combines the efficiency of manual systems with the convenience of automatic shifting.
Maintenance Requirements
Each type of transmission requires specific maintenance to ensure smooth operation:
- Regular fluid checks and changes are vital for all transmission types to prevent overheating and wear.
- For automatic and CVT systems, replacing the filter periodically can improve performance.
- Manual transmissions benefit from occasional clutch adjustments and fluid replacements to maintain responsiveness.
- Monitoring for leaks and unusual noises is crucial for early detection of potential issues.
By adhering to the recommended maintenance practices for each transmission type, owners can ensure a reliable driving experience and avoid costly repairs in the future.
Safety Features and Enhancements
This section focuses on the vital elements that contribute to the overall protection of occupants in vehicles, emphasizing advancements that have been integrated into automotive design. Understanding these features is essential for ensuring a secure driving experience.
Modern automobiles are equipped with various safety enhancements that address both active and passive protection measures:
- Active Safety Systems: These include technologies designed to prevent accidents, such as:
- Anti-lock braking systems (ABS)
- Traction control
- Electronic stability control (ESC)
- Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS)
- Passive Safety Features: These elements are crucial in minimizing injury during an accident. Key components consist of:
- Multiple airbags for occupant protection
- Reinforced passenger compartments
- Energy-absorbing crumple zones
- Three-point seatbelts with pretensioners
In addition to these features, ongoing developments in materials and technology enhance overall safety performance, ensuring that vehicles meet stringent safety standards.
By prioritizing these enhancements, manufacturers aim to provide a more secure environment for drivers and passengers alike, contributing to a reduction in accident-related injuries and fatalities.