Comprehensive Guide to GMC Savana Repair Manual

Understanding the intricacies of vehicle upkeep is essential for any owner. Whether you are a seasoned mechanic or a novice enthusiast, having access to a detailed resource can significantly enhance your ability to address various challenges. This segment delves into essential procedures, troubleshooting techniques, and general knowledge that empower individuals to maintain their vehicles effectively.
Equipping yourself with the right information is crucial for tackling repairs and ensuring optimal performance. From routine inspections to in-depth technical fixes, having a structured approach allows you to navigate potential issues with confidence. This guide aims to provide a thorough overview that can assist in making informed decisions regarding your vehicle’s care.
Incorporating practical advice and insights into common problems can save time and reduce costs associated with professional services. By familiarizing yourself with the necessary steps and recommended practices, you can cultivate a proactive attitude towards vehicle maintenance. This resource is designed to serve as a reliable companion throughout your automotive journey.
Understanding GMC Savana Models

This section aims to provide insights into the various configurations of a popular van, focusing on their unique features and specifications. Each variant is designed to cater to different needs, from passenger transport to cargo hauling, making it essential to understand their distinct characteristics.
The vehicle line offers a range of options, including different engine types, capacities, and configurations. These variations allow users to select a model that best suits their requirements, whether for personal use, business applications, or specialized services.
In addition to performance attributes, the models also differ in terms of interior space, technology features, and safety systems. Understanding these aspects can greatly influence the decision-making process when choosing the right vehicle for specific tasks.
Overall, a comprehensive knowledge of the different models and their capabilities can enhance ownership experience and optimize functionality for various applications.
Common Issues with GMC Savana

Understanding typical problems associated with this vehicle can help owners maintain its performance and longevity. Many users report encountering a range of challenges, from mechanical failures to electrical issues. Addressing these concerns promptly can prevent more serious complications down the line.
Engine Performance Problems

One of the most frequent complaints relates to engine performance. Drivers often experience issues such as rough idling, reduced power, or stalling. These symptoms can stem from various sources, including fuel delivery problems, clogged filters, or malfunctioning sensors. Regular maintenance checks can assist in identifying these issues early.
Transmission Difficulties
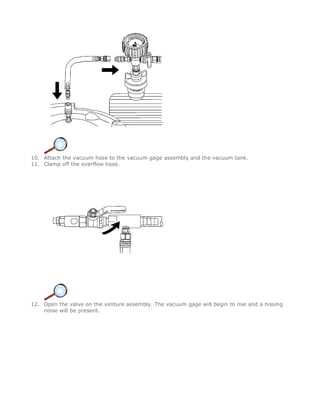
Another common area of concern is transmission performance. Owners may notice slipping gears, delayed shifting, or unusual noises during operation. Such problems may be linked to low fluid levels, worn components, or electronic malfunctions. Addressing these issues as soon as they arise is crucial for ensuring a smooth driving experience and preventing further damage.
Essential Tools for Vehicle Repairs
Having the right instruments is crucial for any automotive maintenance task. A well-equipped workshop allows for efficient troubleshooting and ensures that each component is handled correctly. Understanding which tools to have on hand can make the difference between a simple fix and a prolonged process.
Basic Hand Tools

Every vehicle enthusiast should have a collection of essential hand tools. Wrenches and socket sets are indispensable for loosening and tightening various fasteners. Additionally, pliers and screwdrivers in different sizes cater to a range of applications, from adjusting small parts to larger assemblies. A reliable hammer and a set of chisels can also prove useful in more demanding tasks.
Diagnostic Equipment
To effectively assess vehicle issues, diagnostic equipment is essential. A good OBD-II scanner provides insights into engine performance and error codes, enabling timely identification of problems. Additionally, a multimeter is vital for electrical diagnostics, allowing for precise measurements of voltage, current, and resistance. Investing in these tools can significantly enhance one’s ability to maintain and repair automotive systems.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Procedures

Regular upkeep of your vehicle is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Following a structured approach can help identify issues early, maintain safety, and enhance the overall driving experience. This section outlines essential maintenance steps to keep your vehicle in top condition.
Essential Maintenance Tasks
Here are the fundamental tasks you should consider incorporating into your maintenance routine:
| Task | Frequency | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 5,000 miles | Replace engine oil and filter to ensure proper lubrication. |
| Tire Rotation | Every 6,000 miles | Swap front and rear tires to promote even wear. |
| Brake Inspection | Every 10,000 miles | Check brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels. |
| Fluid Levels Check | Monthly | Inspect coolant, transmission, and brake fluids. |
| Battery Maintenance | Every 6 months | Clean terminals and check for corrosion; test battery health. |
Additional Considerations
In addition to the above tasks, regular inspections of belts, hoses, and lights can prevent unexpected breakdowns. Keeping your vehicle clean and addressing any minor issues promptly will contribute to its reliability and aesthetic appeal. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific maintenance intervals.
Electrical Systems in GMC Savana
The electrical systems in commercial vans play a crucial role in ensuring functionality, safety, and comfort. Understanding the components and their interactions is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the various elements that comprise the electrical architecture, highlighting key features and common issues.
Main Components

- Battery: Serves as the primary power source for all electrical systems.
- Alternator: Charges the battery and powers electrical systems when the engine is running.
- Starter Motor: Initiates the engine start sequence by drawing power from the battery.
- Fuses and Relays: Protect circuits from overloads and control the operation of various electrical components.
Common Electrical Issues

- Dead Battery: Often caused by prolonged inactivity or failure of the charging system.
- Faulty Alternator: Can lead to insufficient power supply, causing dim lights and electronic malfunctions.
- Corroded Connections: Poor connectivity can result in intermittent electrical failures.
- Blown Fuses: Indicate overcurrent situations, requiring inspection of affected circuits.
Proper understanding and maintenance of the electrical systems can significantly enhance performance and reliability. Regular checks and prompt repairs are advisable to avoid larger issues down the line.
Engine Troubleshooting Techniques
Diagnosing issues with the power unit requires a systematic approach to identify problems effectively. Understanding the symptoms and employing specific strategies can help pinpoint the root cause of malfunctions, leading to a successful resolution. This section outlines essential techniques for troubleshooting engine-related concerns.
Common Symptoms and Initial Checks
- Unusual noises, such as knocking or rattling
- Reduced power or sluggish acceleration
- Excessive exhaust smoke
- Overheating or abnormal temperature readings
Begin by conducting a visual inspection. Look for leaks, worn belts, or damaged hoses. Ensure all fluid levels are adequate, and check for any error codes using an onboard diagnostics (OBD) scanner.
Diagnostic Techniques

- Fuel System Check: Inspect the fuel pump, filter, and injectors to ensure proper fuel delivery.
- Ignition System Assessment: Examine spark plugs, wires, and coils to verify they are functioning correctly.
- Compression Test: Measure the compression in each cylinder to assess the overall health of the engine.
- Cooling System Evaluation: Check the radiator, thermostat, and hoses for signs of wear or blockage.
By systematically applying these troubleshooting techniques, one can effectively isolate and address engine issues, restoring optimal performance. Always refer to detailed specifications for further guidance as needed.
Brake System Repairs Explained

The brake system is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding the intricacies involved in maintaining and fixing this system can significantly enhance both performance and longevity. This section delves into the various elements of brake system issues and provides insights into troubleshooting and resolving common problems.
| Component | Common Issues | Signs of Failure | Basic Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brake Pads | Wear and tear | Squeaking noises, reduced stopping power | Replace pads as needed |
| Brake Rotors | Warping, corrosion | Vibrations while braking | Resurface or replace rotors |
| Brake Fluid | Contamination, leaks | Soft brake pedal, warning light | Flush and refill fluid |
| Calipers | Sticking, leaking | Uneven wear, pulling to one side | Inspect and replace as necessary |
Regular maintenance and timely intervention are essential for optimal braking performance. Understanding these components and their potential issues can empower vehicle owners to take proactive steps in ensuring a reliable driving experience.
Transmission Maintenance Best Practices

Proper care and regular attention to the transmission system are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle. By adhering to a set of best practices, you can prevent potential issues and extend the life of this vital component.
Regular Fluid Checks
Maintaining the correct fluid level and quality is essential for smooth transmission operation. Follow these steps:
- Check the fluid level monthly, ensuring it falls within the recommended range.
- Inspect the fluid for discoloration or a burnt smell, indicating it may need to be replaced.
- Use the manufacturer’s recommended fluid type to ensure compatibility.
Scheduled Servicing
Adhering to a regular service schedule can prevent costly repairs down the line. Consider the following:
- Change the transmission fluid according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, usually every 30,000 to 60,000 miles.
- Replace the transmission filter during fluid changes to ensure clean fluid circulation.
- Inspect and adjust the linkage regularly to ensure smooth shifting.
By implementing these practices, you can enhance the reliability and efficiency of your transmission system, ultimately contributing to a safer and more enjoyable driving experience.
Diagnosing Cooling System Problems

Understanding issues within the cooling mechanism is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and preventing potential overheating. Identifying the symptoms and sources of these problems can save time and resources, ensuring longevity and efficiency of the vehicle.
Common Symptoms of Cooling System Failures

Several signs can indicate that the cooling system is not functioning correctly. Recognizing these early can lead to more effective troubleshooting.
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Engine Overheating | Low coolant levels, blocked radiator, or malfunctioning thermostat |
| Coolant Leaks | Deteriorated hoses, damaged radiator, or faulty water pump |
| Strange Noises | Air in the system, failing water pump, or loose components |
| Coolant Warning Light | Faulty sensor, low coolant level, or electrical issue |
Troubleshooting Steps

To effectively address cooling system issues, follow a systematic approach. Start by checking the coolant level and inspecting for leaks. Next, assess the radiator and hoses for blockages or wear. Lastly, evaluate the thermostat and water pump functionality to ensure they are operating correctly.
Suspension and Steering Insights
This section delves into the vital components that ensure a smooth ride and responsive handling. Understanding these systems is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and safety.
The suspension system plays a key role in absorbing shocks and providing stability. It consists of various elements that work together to enhance comfort and control.
- Shock Absorbers: These devices dampen the impact of bumps and uneven surfaces.
- Struts: Integral to the suspension system, struts help support the vehicle’s weight and improve handling.
- Springs: They assist in maintaining the vehicle’s height and provide necessary flexibility.
Effective steering is equally important for maneuverability and safety. Key components in this system include:
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for drivers to control direction.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the steering mechanism.
- Rack and Pinion: Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement of the wheels.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these systems are essential for optimal performance. Ensuring proper alignment and checking for wear can prevent issues and enhance driving experience.
Fuel System Service Recommendations
Maintaining the fuel delivery system is crucial for optimal vehicle performance. Regular inspection and timely service can prevent potential issues, ensuring efficiency and longevity. Below are key recommendations for servicing the fuel system, highlighting important components and their care.
Routine Inspection
Conducting periodic inspections of the fuel system can help identify wear or damage before they lead to significant problems. Focus on the following components:
| Component | Inspection Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Filter | Every 15,000 miles | Replace if clogged or damaged. |
| Fuel Pump | Every 30,000 miles | Listen for unusual noises during operation. |
| Fuel Injectors | Every 20,000 miles | Clean or replace if performance decreases. |
Fuel Quality Management
Using high-quality fuel can significantly impact engine efficiency and overall performance. It’s advisable to avoid low-grade fuel and regularly check for contaminants. Implementing a fuel system cleaner can also help maintain injector cleanliness and prevent buildup.
Using Diagnostic Tools Effectively
Effective utilization of diagnostic instruments is crucial for identifying and resolving issues in vehicles. These tools enable technicians to monitor various systems and components, providing valuable insights that facilitate accurate troubleshooting. Understanding how to leverage these devices can significantly enhance repair efficiency and accuracy.
Before diving into diagnostics, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the specific tools available and their functionalities. Proper selection and application of these instruments can lead to quicker identification of faults, reducing both time and costs associated with repairs.
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| OBD-II Scanner | Reads error codes from the vehicle’s computer | Connect and ensure proper communication; reset codes after repairs |
| Multimeter | Measures electrical values like voltage and resistance | Check battery and circuit integrity; calibrate regularly |
| Pressure Gauge | Monitors fluid pressures in various systems | Ensure correct connections; compare readings against manufacturer specifications |
Incorporating these diagnostic tools into your workflow not only aids in quicker identification of issues but also contributes to a more structured approach to vehicle maintenance. By adhering to best practices and continually updating your knowledge of these instruments, you can improve overall diagnostic accuracy and service quality.