Comprehensive Guide to Repairing the 1NZ-FE Engine

In the world of automotive mechanics, understanding the intricacies of propulsion systems is essential for both enthusiasts and professionals alike. This section delves into the nuances of maintaining a specific power unit, offering insights and practical advice to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Whether you are a seasoned mechanic or a novice looking to enhance your skills, mastering the complexities of this unit will empower you to tackle a variety of challenges. Through detailed explanations and step-by-step instructions, you will gain the knowledge necessary to troubleshoot and resolve common issues effectively.
From routine checks to intricate overhauls, this guide emphasizes the importance of precision and attention to detail. With a focus on best practices and essential techniques, readers will be equipped to navigate the various aspects of upkeep, ensuring reliability and efficiency in their automotive endeavors.
Overview of the 1NZ-FE Engine
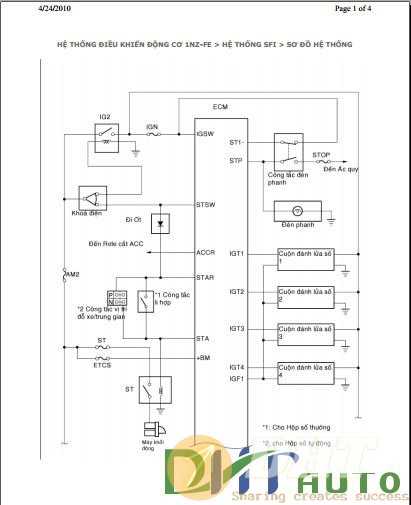
This section provides a comprehensive look at a specific type of compact power unit commonly used in various vehicles. Known for its efficiency and reliability, this configuration has gained popularity in the automotive industry due to its balanced performance and environmental considerations.
The design of this power unit includes several notable features that contribute to its functionality:
- Compact size, making it suitable for smaller vehicles.
- Lightweight construction, enhancing fuel efficiency.
- Innovative fuel management system for optimized combustion.
- Advanced cooling technology to maintain operational stability.
This power unit typically operates using a four-cylinder layout, allowing for smooth performance across various driving conditions. Its architecture supports various transmission types, further increasing its versatility.
Some key specifications to note include:
- Displacement: Approximately 1.5 liters.
- Maximum horsepower: Around 105 hp.
- Torque output: Approximately 100 lb-ft.
Overall, this power unit exemplifies a balance between performance and efficiency, making it a favored choice among manufacturers and consumers alike.
Common Issues and Symptoms
This section addresses frequent problems and their corresponding indicators that may arise in the functioning of the unit. Recognizing these signs early can significantly aid in maintaining optimal performance and preventing more severe complications.
Performance Degradation
One of the primary symptoms is a noticeable drop in performance. Drivers might experience reduced acceleration, sluggishness, or a general lack of power. These issues can often stem from various factors, including fuel delivery problems or malfunctions in the ignition system.
Unusual Noises and Vibrations
Another common issue involves the emergence of strange sounds or vibrations during operation. Unexplained knocking, rattling, or excessive shaking can indicate underlying mechanical problems. It’s essential to address these concerns promptly, as they can lead to more extensive damage if left unresolved.
In summary, being aware of these typical issues and their symptoms is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the unit. Regular monitoring and timely intervention can prevent minor concerns from escalating into major faults.
Tools Required for Repair

To effectively address maintenance tasks, having the right instruments at hand is crucial. Proper tools not only enhance efficiency but also ensure accuracy in every step of the process. A well-equipped workspace can make the difference between a smooth operation and unnecessary complications.
Essential tools include:
- Wrenches – for loosening and tightening various components.
- Screwdrivers – for handling screws in different sizes and types.
- Torque wrench – to apply the correct amount of force to bolts.
- Jack stands – for safely lifting the vehicle during the procedure.
- Oil filter wrench – for easy removal of filters.
Having these tools will ultimately streamline your workflow and ensure a thorough job is completed.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
Disassembling a complex mechanical unit requires careful planning and attention to detail. This section outlines a systematic approach to taking apart the assembly, ensuring that each step is executed with precision. Following this method will help in organizing the components and facilitate a smoother reassembly.
1. Preparation: Begin by gathering all necessary tools and equipment. A clean workspace is essential to prevent the loss of small parts. Make sure to have containers for screws and other fasteners to keep everything organized.
2. Documentation: Take photographs or notes of the assembly before disassembly. This will serve as a valuable reference when reassembling the unit.
3. Removing Accessories: Start by detaching any external attachments, such as belts, hoses, and electrical connectors. Carefully label each component to ensure easy identification later.
4. Fastener Removal: Use the appropriate tools to remove bolts and screws. Work systematically, starting from the outer edges and moving inward. Avoid stripping fasteners by applying consistent pressure.
5. Component Separation: Once the fasteners are removed, gently separate the parts. Use a soft mallet if necessary, but avoid using excessive force to prevent damage.
6. Inspection: As each component is removed, inspect for wear or damage. This will provide insight into necessary replacements or repairs during the reassembly phase.
7. Organization: Keep all components in labeled containers. This will streamline the reassembly process and minimize confusion when putting everything back together.
By adhering to these steps, you can ensure a methodical disassembly process that lays the groundwork for a successful reassembly.
Inspecting Engine Components

Thorough examination of mechanical parts is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This process involves a careful assessment of various elements to identify wear, damage, or any signs of malfunction. Regular inspections can help prevent unexpected failures and maintain efficiency.
Key components to evaluate include:
- Pistons
- Crankshaft
- Camshaft
- Valves
- Gaskets and seals
During the inspection, consider the following steps:
- Visual Inspection: Look for any visible cracks, corrosion, or unusual wear patterns.
- Measurement: Use precision tools to measure critical dimensions, ensuring components are within specified tolerances.
- Surface Condition: Check for smoothness and integrity of surfaces, particularly in contact areas.
- Functionality Testing: If applicable, assess the operation of moving parts to confirm they function smoothly without excessive resistance.
By adhering to these guidelines, one can effectively evaluate the condition of essential components, paving the way for informed decisions regarding maintenance or replacement. Regular checks not only enhance reliability but also contribute to overall performance enhancements.
Replacing Gaskets and Seals
Proper maintenance of internal components is crucial for optimal performance. Over time, gaskets and seals can degrade, leading to leaks and reduced efficiency. This section outlines the importance of timely replacement and the steps involved in ensuring a tight seal and preventing unwanted fluid loss.
Understanding the Role
Gaskets and seals serve as barriers between various parts, preventing fluid exchange and contamination. Their integrity is essential for maintaining pressure and ensuring smooth operation. Regular inspection can help identify wear and tear, allowing for proactive measures to be taken.
Steps for Replacement
To begin, carefully dismantle the relevant components, taking care to avoid damage. Once exposed, remove the old gaskets and seals, ensuring that all remnants are cleaned off the surfaces. Applying a suitable sealant may enhance the effectiveness of the new parts. Position the new gaskets and seals accurately before reassembling the components, ensuring everything is aligned correctly.
Final Checks
After assembly, it is important to run a thorough check for any signs of leakage. Monitor performance closely in the initial stages to ensure the new parts are functioning as intended. Regular maintenance and timely replacements can significantly extend the lifespan of internal systems.
Rebuilding the Cylinder Head
Revitalizing the upper section of a power unit is a critical task that can significantly enhance performance and longevity. This process involves meticulous attention to detail, ensuring that each component is meticulously inspected and, if necessary, restored to optimal condition. A thorough understanding of the assembly’s structure and functionality is essential for achieving a successful outcome.
Disassembly and Inspection
The initial step involves carefully taking apart the assembly to access all internal parts. Each piece should be examined for wear, cracks, or other damage. Pay close attention to valve seats and guides, as well as the surface where the head meets the block. Cleaning all components is crucial, as contaminants can lead to future failures.
Reassembly and Testing
Once all parts are evaluated and any necessary repairs are completed, reassembly can commence. Proper torque specifications must be followed to ensure a tight seal. After the unit is reassembled, conducting a series of tests is vital to verify functionality. This includes checking for leaks and ensuring that all systems operate harmoniously.
Timing Chain Replacement Procedure
Replacing the timing chain is a critical task that ensures the synchronization of various components within the assembly. This process requires attention to detail and adherence to specific steps to maintain optimal performance and prevent potential issues.
Before starting, gather all necessary tools and parts. It’s essential to work in a clean environment to avoid contamination. Make sure the vehicle is securely elevated, and disconnect the battery to ensure safety during the procedure.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Remove the cover that protects the timing chain. This typically involves unscrewing several bolts and gently lifting the cover off. |
| 2 | Locate the timing chain and observe the alignment marks on the gears. It’s crucial to mark the current position for accurate reinstallation. |
| 3 | Loosen the tensioner, allowing the chain to be removed easily. Take care to avoid damaging surrounding components during this step. |
| 4 | Carefully remove the old timing chain, noting the orientation and placement of any guides or tensioners. |
| 5 | Install the new chain, ensuring it is positioned correctly according to the previously marked alignment. Double-check the tension and guide placement. |
| 6 | Reattach the tensioner and verify that it is functioning properly. Ensure all bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. |
| 7 | Replace the cover and secure it in place. Finally, reconnect the battery and perform a functionality test to confirm everything is working smoothly. |
Following these steps carefully will lead to a successful replacement, enhancing the longevity and performance of the unit. Always consult specific guidelines or technical documentation for detailed information on particular requirements.
Reassembly Tips and Techniques
Reassembling components after disassembly requires precision and attention to detail. Following a systematic approach not only ensures optimal performance but also prolongs the lifespan of the entire system. Here are some valuable strategies to guide you through the reassembly process.
1. Organize Your Workspace: Before starting, clear your workspace of any clutter. Arrange tools and parts methodically to avoid confusion during the assembly. Labeling components can also help maintain order.
2. Refer to Documentation: Keep relevant diagrams or notes handy. Visual aids can provide critical information about the positioning and alignment of various parts, reducing the risk of errors.
3. Clean Components: Before reassembling, ensure all parts are clean and free of debris. This not only helps in achieving a snug fit but also prevents potential damage during operation.
4. Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts as specified. Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, enhancing the efficiency and longevity of the assembly.
5. Tightening Sequence: Follow the recommended tightening sequence and torque specifications. This ensures even pressure distribution, which is crucial for maintaining structural integrity.
6. Double-Check Alignment: Before securing components, check that everything is aligned correctly. Misalignment can lead to complications, so take the time to adjust as needed.
7. Final Inspection: After assembly, conduct a thorough inspection. Look for any loose parts, missed connections, or other issues that may have arisen during the process.
By implementing these techniques, you can achieve a successful reassembly that meets both performance standards and reliability expectations.
Testing Engine Performance After Repair
Assessing the functionality of a power unit following maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal operation and reliability. This process involves a series of evaluations to determine whether the necessary adjustments and replacements have effectively restored the system’s performance to its intended standards.
Initial Observations
Begin by conducting visual inspections and listening for unusual sounds during idle and acceleration. Check for any leaks or irregularities in fluid levels. Monitoring exhaust emissions can also provide insights into the efficiency of combustion and overall health of the unit.
Performance Metrics
Utilize diagnostic tools to measure key parameters such as power output, fuel consumption, and responsiveness. Acceleration tests can reveal how well the system performs under load, while RPM readings will help identify any inconsistencies. Comparing these metrics to manufacturer specifications will highlight any lingering issues and validate the success of the service performed.
Maintenance Practices for Longevity
Ensuring the long-term performance of your vehicle requires consistent and attentive care. By implementing a series of effective maintenance strategies, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your machinery and enhance its efficiency. This section outlines key practices that contribute to sustained reliability and performance.
Regular Inspections
Conducting routine evaluations is crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Here are some essential components to check:
- Fluid levels: Regularly monitor oil, coolant, and other vital fluids.
- Belts and hoses: Look for signs of wear or cracks.
- Filters: Ensure air and fuel filters are clean and replaced as needed.
- Battery: Check for corrosion and ensure terminals are secure.
Scheduled Maintenance
Adhering to a predefined maintenance schedule helps keep everything in optimal condition. Consider the following practices:
- Change oil and filters every specified interval.
- Rotate tires to promote even wear.
- Inspect brake components regularly for efficiency.
- Flush coolant and replace as recommended.
By committing to these maintenance practices, you can enhance the reliability and longevity of your vehicle, ultimately leading to a smoother and more enjoyable driving experience.
Resources for Further Learning
Expanding your knowledge in automotive maintenance and technical skills can greatly enhance your understanding and ability to work on various vehicle systems. This section provides valuable resources for those looking to deepen their expertise and gain hands-on experience.
Books and Publications: A wide range of literature exists that covers various aspects of vehicle systems. Look for titles that focus on diagnostics, performance tuning, and overall maintenance practices. Many of these resources offer in-depth illustrations and detailed instructions, making complex concepts more accessible.
Online Forums and Communities: Joining online platforms where enthusiasts and professionals discuss troubleshooting and enhancements can be incredibly beneficial. These communities often share tips, experiences, and advice that can help you navigate challenges and learn from others’ successes.
Video Tutorials: Numerous educational channels on platforms like YouTube provide visual demonstrations of processes and techniques. Watching experienced individuals perform tasks can clarify steps and methods that may seem daunting when reading about them.
Workshops and Classes: Local community colleges or automotive schools frequently offer courses tailored to various skill levels. Participating in hands-on workshops can provide practical experience and opportunities to work under the guidance of knowledgeable instructors.
By utilizing these resources, you can continuously improve your skills and stay updated on the latest advancements in automotive technology.