Structural Repair Manual Overview

Ensuring the longevity and safety of an aircraft often requires meticulous attention to its framework. Over time, various elements may experience wear, necessitating specific actions to maintain optimal performance and safety. This section delves into essential practices for addressing these needs, focusing on precision and reliability.
With a comprehensive set of techniques and instructions, this guide helps you navigate through the procedures required to reinforce and sustain the core components of an airframe. By following the outlined recommendations, you can ensure that all maintenance tasks are carried out effectively, adhering to the highest standards of aviation upkeep.
Understanding how to approach these procedures correctly is key to maintaining an aircraft’s structural soundness. From initial assessments to detailed step-by-step processes, the information provided here aims to equip you with the necessary insights and guidelines to execute tasks with confidence.
Understanding Structural Repair Procedures
Comprehensive knowledge of restoration techniques is essential for maintaining the integrity and functionality of various constructions. This section aims to provide a clear overview of the methods and practices involved in addressing issues within different frameworks. Whether dealing with minor fixes or extensive renovations, it’s important to understand the appropriate steps to ensure safety and durability.
Key Concepts in Restoration Techniques
Effective solutions often begin with a detailed analysis of the issue, identifying weak points that need attention. Once the assessment is complete, a plan can be devised to address these areas efficiently. Using the right tools and materials is crucial, as it ensures the longevity of the work and minimizes future complications.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices

Preventing future deterioration is as important as fixing existing issues. Regular maintenance checks, combined with proper handling and timely upgrades, help to prolong the life of structures. By adhering to best practices, it is possible to avoid costly interventions and ensure the long-term resilience of the construction.
Key Components of Repair Manuals

A well-organized guide for maintenance encompasses essential details that help users understand the process of restoring equipment or machinery. It provides comprehensive insights into necessary procedures, step-by-step instructions, and safety measures, ensuring that users can efficiently address technical issues. The content within these guides is structured to offer clear, accessible directions for various types of servicing tasks.
Detailed Descriptions and Diagrams
One of the main elements is the inclusion of clear descriptions paired with visual aids. Diagrams and illustrations serve to make complex tasks easier to comprehend, enabling users to follow along accurately. These visual representations are crucial for highlighting intricate parts and showing how they should be managed during maintenance.
Step-by-Step Instructions
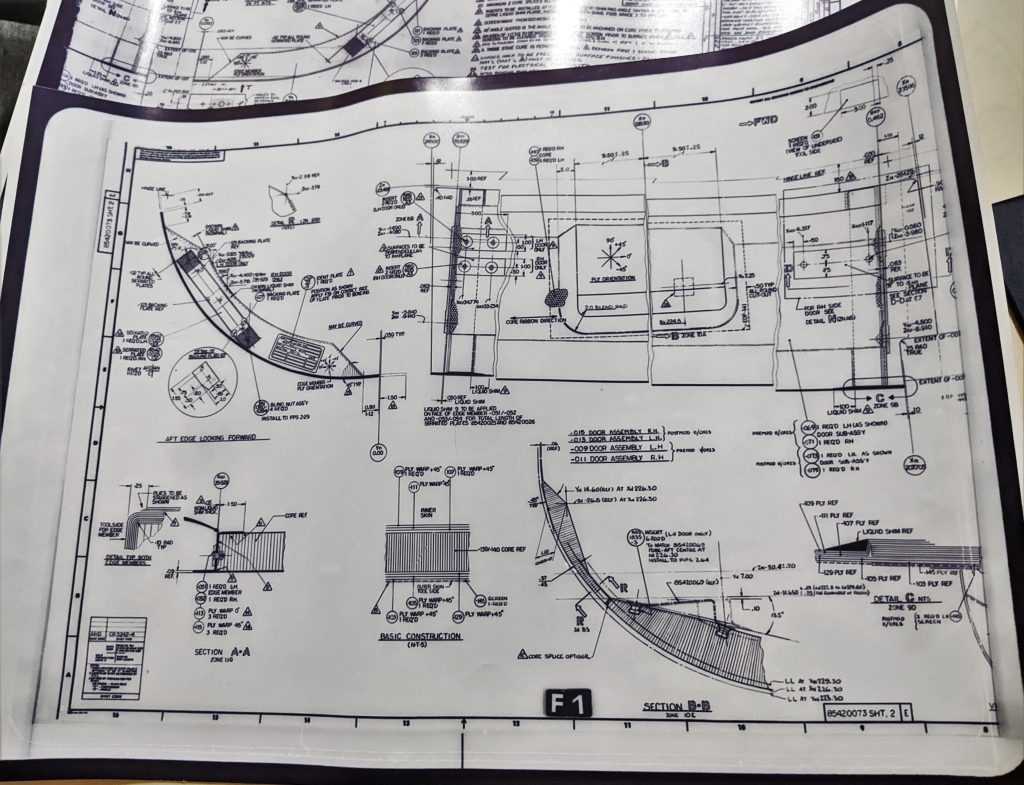
Another vital aspect is the presence of step-by-step guidance that breaks down each task into manageable actions. This organized approach ensures that users can proceed with confidence, reducing the likelihood of errors. Each stage is usually accompanied by tips to enhance understanding and efficiency, making the process smoother and more straightforward.
Inspection Techniques for Structural Integrity
Ensuring the longevity and safety of various constructions requires regular assessments of their overall condition. By applying effective examination methods, potential vulnerabilities can be identified before they escalate, helping to maintain the reliability of the construction over time. This section outlines the key approaches to assessing the overall state of physical frameworks, focusing on accuracy and thoroughness during each stage of the process.
Visual Examination
The initial step in the assessment process involves a comprehensive visual check. Inspectors carefully observe all accessible areas to detect any visible signs of wear, such as cracks, corrosion, or deformation. This technique is essential for identifying surface-level issues that might indicate deeper underlying problems. It also serves as a foundation for deciding which further testing methods may be required.
Non-Destructive Testing Methods
When deeper analysis is necessary, non-destructive techniques come into play. These methods, including ultrasonic testing, radiography, and magnetic particle inspections, allow evaluators to examine the inner layers of the framework without causing any damage. They are crucial for detecting hidden flaws that are not apparent during a standard v
Documentation Essentials for Repair Processes
Effective technical documentation plays a crucial role in ensuring that maintenance tasks are carried out accurately and efficiently. By providing clear, step-by-step instructions, it minimizes the risk of errors, enhances safety, and ensures consistency across various tasks. Detailed guides support technicians by offering a structured approach to complex procedures.
- Clear Instructions: Concise and straightforward instructions help technicians understand each step without confusion, leading to better outcomes.
- Illustrations and Diagrams: Visual aids, such as diagrams and annotated images, make it easier to follow complex tasks and identify parts or tools needed.
- Comprehensive Component Lists: Including lists of necessary parts, tools, and materials ensures that all resources are readily available before starting the task.
- Safety Guidelines: Highlighting essential safety protocols prevents accidents and maintains a secure working environment.
- Quality Control Checkpoints: Adding quality control points allows for verification at crucial stages, ensuring that each step is completed correctly.
- Start by defining the objective of the task and any prerequisites that should be met.
- List the necessary equipment
Common Issues in Aircraft Structures
Aircraft face various challenges during their operational lifespan, which can lead to wear, damage, and other concerns. Understanding these issues is crucial for ensuring safety and performance, as they can affect different parts of the craft, ranging from the wings to the fuselage.
- Corrosion: Prolonged exposure to environmental elements, such as moisture and salt, can lead to metal degradation. This is particularly problematic in areas with constant contact with water, like landing gear and lower fuselage sections.
- Fatigue Cracks: Continuous stress cycles during takeoffs, landings, and turbulence can cause tiny cracks to develop over time. If left unchecked, these cracks can grow and compromise the integrity of key parts.
- Material Deformation: Excessive loads or unexpected forces might cause bending or warping in some parts. This deformation can alter aerodynamics and impact the overall performance of the aircraft.
- Loose Fasteners: Vibration during flights can gradually loosen bolts, screws, and rivets, leading to gaps and potential component failure. Regular inspections help identify and address such issues.
- Impact Damage: Birds, debris, and minor collisions on the ground can cause dents or cracks in various areas, such as wings and the nose. While these
Material Selection for Effective Repairs
Choosing the right materials is crucial for achieving successful restoration outcomes. The effectiveness of a renovation process greatly depends on the characteristics of the chosen substances, which must be compatible with the existing components and environmental conditions. This section emphasizes the importance of thoughtful material selection to enhance durability and functionality.
Several factors should be considered when selecting materials, including strength, weight, thermal properties, and resistance to environmental factors. The following table outlines common materials and their applications:
Material Properties Common Uses Steel High strength, durable Framework, reinforcements Concrete Robust, fire-resistant Foundations, walls Wood Lightweight, versatile Framework, finishes Fiberglass Corrosion-resistant, flexible Pipes, panels Aluminum Lightweight, resistant to corrosion Framework, cladding Ultimately, a strategic approach to material selection can significantly influence the longevity and performance of any enhancement project.
Tools and Equipment for Structural Work
When undertaking any form of construction or modification, the selection of appropriate instruments and devices is crucial for achieving optimal results. The right tools not only enhance efficiency but also ensure safety during the execution of tasks. Understanding the variety of available options can significantly influence the quality of the completed project.
Essential Instruments
Among the fundamental instruments required for construction activities are measuring devices, cutting tools, and fastening mechanisms. Precision measuring tools, such as tape measures and laser levels, enable accurate alignment and dimensions. Additionally, cutting implements, including saws and chisels, are indispensable for shaping materials effectively. Fasteners, such as screws and nails, play a vital role in joining components securely.
Safety Gear and Equipment
Ensuring safety on-site is paramount. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential to safeguard workers from potential hazards. This includes hard hats, safety glasses, and gloves. Moreover, scaffolding and ladders are crucial for accessing elevated areas safely, allowing workers to perform tasks without compromising their well-being.
Safety Protocols During Repair Operations
Ensuring the well-being of personnel while conducting maintenance tasks is of utmost importance. Adhering to specific guidelines minimizes risks and promotes a secure working environment. This section outlines essential practices to follow to maintain safety throughout the entire process.
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment before starting any task to identify potential hazards.
- Utilize appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including helmets, gloves, and safety goggles.
- Ensure all tools and equipment are in good condition and properly maintained.
- Establish clear communication protocols among team members to facilitate effective collaboration.
By implementing these measures, the likelihood of accidents can be significantly reduced, fostering a culture of safety and responsibility among all individuals involved.
- Stay aware of your surroundings and any changing conditions that may arise during operations.
- Follow established emergency procedures and know the location of first aid kits and emergency exits.
- Report any unsafe conditions or equipment malfunctions immediately to supervisors.
- Engage in regular training sessions to stay updated on safety practices and protocols.
Commitment to these safety protocols not only protects individuals but also enhances the efficiency and quality of the overall work conducted.
Assessing Damage Severity and Solutions
Determining the extent of harm is crucial for developing effective strategies to address issues within a given framework. A thorough evaluation not only identifies the nature of the damage but also helps prioritize actions based on urgency and potential impact. This initial assessment sets the stage for subsequent interventions, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and appropriately.
Evaluating Extent of Harm

To accurately gauge the level of damage, various factors must be considered. Visual inspections can reveal surface irregularities, while more in-depth assessments may require advanced tools and techniques. By categorizing the severity into distinct levels–minor, moderate, or critical–professionals can formulate tailored approaches that align with the specific conditions observed.
Formulating Effective Strategies
Once the assessment is complete, the next step involves devising actionable solutions. This may include temporary measures to stabilize the environment, as well as long-term strategies aimed at restoration. Collaboration among experts across various disciplines ensures that the selected solutions are holistic, addressing both immediate concerns and future resilience.
Repair Guidelines for Composite Materials
This section provides essential recommendations for addressing issues related to composite substances. It is crucial to understand the unique properties of these materials to ensure effective intervention strategies that maintain their performance and longevity.
Prior to commencing any work, thorough assessment and understanding of the damage are vital. Proper identification of the type of composite and the extent of degradation will dictate the approach to be taken. Below are general steps to follow:
Step Description 1 Conduct a detailed inspection to identify cracks, delamination, or other forms of deterioration. 2 Choose suitable materials and techniques for the intended intervention, taking into account the specific type of composite. 3 Prepare the damaged area by cleaning and ensuring proper adhesion surfaces are established. 4 Apply the chosen materials according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring even distribution. 5 Allow sufficient curing time before subjecting the composite to any load or stress. Following these guidelines will help in maintaining the integrity and functionality of composite materials. Regular monitoring and maintenance can also prevent future complications.
Maintaining Compliance with Aviation Standards
Ensuring adherence to industry regulations is vital for the safety and reliability of aircraft operations. Organizations must implement systematic approaches to meet the requirements set forth by governing bodies. This commitment not only enhances safety but also fosters trust among stakeholders and customers.
Regular Audits and Inspections
Conducting frequent assessments is essential for identifying potential non-compliance issues. These evaluations should cover all aspects of operations, including maintenance practices, training procedures, and documentation processes. By addressing discrepancies promptly, organizations can mitigate risks and enhance overall operational integrity.
Continuous Training and Education
Investing in ongoing training for personnel ensures that staff remain knowledgeable about current regulations and best practices. Workshops, seminars, and certification programs play a crucial role in equipping employees with the necessary skills to uphold compliance. A well-informed workforce is key to maintaining high standards within the aviation sector.
Quality Control in Repair Procedures
Ensuring the highest standards during the process of restoration is crucial for achieving lasting results. This phase involves a systematic approach to verifying that all tasks are conducted accurately and meet specified criteria. Effective oversight not only enhances the quality of work but also minimizes the risk of future issues.
Key Aspects of Quality Oversight

- Inspection Protocols: Establishing thorough guidelines for evaluating each stage of the restoration process.
- Training and Expertise: Ensuring that all personnel involved possess the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their duties competently.
- Documentation: Keeping detailed records of all procedures, inspections, and any deviations from standard practices.
Benefits of Implementing Quality Assurance
- Enhanced Durability: Work that meets stringent standards tends to last longer and require fewer interventions.
- Increased Client Satisfaction: Delivering high-quality outcomes leads to greater trust and satisfaction among clients.
- Reduced Costs: By preventing errors and rework, organizations can save on expenses associated with future corrections.
Training Requirements for Repair Technicians

To ensure the proficiency of technicians in the field, a comprehensive training framework is essential. This framework encompasses a variety of skills and knowledge areas, enabling professionals to perform their duties effectively and safely.
The following key components are vital in the training of technicians:
- Theoretical Knowledge: Understanding the underlying principles of various systems and materials is crucial.
- Practical Skills: Hands-on experience with tools and equipment enhances a technician’s ability to execute tasks accurately.
- Safety Protocols: Familiarity with safety standards and practices is necessary to mitigate risks during operations.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Technicians should be equipped with strategies to identify issues and devise effective solutions.
- Continuous Education: Ongoing training is important to stay updated with advancements in technology and methods.
Moreover, certifications and specialized courses can further validate a technician’s competence in specific areas. Engaging in mentorship programs can also facilitate knowledge transfer and practical learning from experienced professionals.