Comprehensive Guide to Repairing the Toyota 1JZ GTE Engine

The pursuit of automotive excellence often leads enthusiasts to delve into the intricacies of high-performance power units. Understanding the nuances of these mechanical marvels can enhance both the longevity and efficiency of any vehicle. This section aims to provide a thorough overview of the essential steps and considerations involved in maintaining and revitalizing these sophisticated systems.
For those looking to embark on a journey of rejuvenation, it is crucial to familiarize oneself with the various components and their interrelations. Each segment plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal functionality, and knowledge of their specific characteristics is key to achieving desired results. From diagnosing common issues to executing meticulous upgrades, this guide serves as a valuable resource for both novices and seasoned experts alike.
Additionally, recognizing the significance of precision in assembly and disassembly processes cannot be overstated. The complexity of modern machinery demands a careful approach to avoid costly mistakes and ensure the harmonious operation of all parts. With the right tools, techniques, and insights, anyone can unlock the full potential of their power unit, transforming their driving experience into one of unparalleled satisfaction.
Toyota 1JZ GTE Overview
This section provides a comprehensive understanding of a renowned powerplant that has gained a dedicated following among automotive enthusiasts. Known for its robust performance and engineering excellence, this unit has become a popular choice for those seeking a blend of reliability and power in their vehicles.
Developed in the late 1980s, this power unit has established itself as a key player in the realm of high-performance vehicles. Its notable characteristics include:
- Inline six-cylinder configuration
- Turbocharging for enhanced power output
- Strong aftermarket support
- Versatile applications across various models
Many enthusiasts appreciate its capability to deliver exceptional performance while maintaining manageable operating characteristics. Additionally, this unit is praised for its durability, often allowing for significant tuning and modifications without compromising longevity.
Overall, this power source represents a blend of innovation and tradition, making it a favorite among tuners and casual drivers alike.
Common Issues with 1JZ GTE
When it comes to high-performance powertrains, several challenges can arise that may affect overall performance and reliability. Understanding these common pitfalls is crucial for enthusiasts and mechanics alike to ensure optimal function and longevity. This section highlights prevalent concerns that can arise, along with their potential impacts.
One of the frequent problems is oil leakage, which can stem from various seals and gaskets wearing out over time. This issue not only leads to loss of vital lubricants but can also cause significant damage if left unaddressed. Regular checks can help identify and rectify such leaks before they escalate.
Another notable concern involves overheating. Factors such as a failing cooling system or blocked radiator can contribute to excessive temperatures, risking severe damage. It’s essential to maintain the cooling system meticulously to prevent this from occurring.
Furthermore, misfiring cylinders can create performance inconsistencies. This issue often results from faulty ignition components or fuel delivery problems. Ensuring that spark plugs and injectors are in good condition is key to maintaining smooth operation.
Lastly, turbocharger issues can arise, particularly with older models. Signs such as excessive smoke or unusual noises may indicate that the turbo is failing. Regular inspections can help catch these issues early, preserving the performance of the entire system.
Essential Tools for Engine Repair

When embarking on an intricate mechanical project, having the right instruments at hand is crucial for success. The following tools will help facilitate various tasks, ensuring efficiency and precision during the process.
Basic Hand Tools
- Socket Set: A comprehensive socket set allows for easy access to various fasteners.
- Wrenches: Both adjustable and fixed wrenches are essential for loosening and tightening components.
- Screwdrivers: A variety of Phillips and flathead screwdrivers is necessary for handling different screws.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and locking pliers provide versatility in gripping and manipulating parts.
Specialized Equipment

- Torque Wrench: Ensures fasteners are tightened to the correct specifications.
- Compression Tester: Evaluates the health of the cylinders and identifies potential issues.
- Oil Pressure Gauge: Monitors oil flow and pressure, crucial for proper lubrication.
- Timing Light: Assists in adjusting ignition timing for optimal performance.
Equipping yourself with these essential tools not only simplifies the task at hand but also enhances the overall outcome of your mechanical endeavors.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
Understanding the intricate procedure of dismantling a complex mechanical assembly is crucial for effective maintenance and restoration. This section will guide you through the essential steps to safely and efficiently disassemble the unit, ensuring that each component is handled with care.
- Preparation:
- Gather necessary tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers.
- Ensure a clean and organized workspace to avoid misplacing parts.
- Consult relevant documentation for specific instructions and diagrams.
- Initial Inspection:
- Examine the exterior for any signs of damage or wear.
- Document the current state of the assembly with photographs for reference.
- Remove External Components:
- Detach accessories such as brackets, hoses, and electrical connectors.
- Label each component to facilitate reassembly later.
- Access the Core:
- Unscrew and remove protective covers or shields.
- Take care to note the orientation and position of each piece.
- Dismantling Internal Parts:
- Gradually remove internal components, starting from the outer layers.
- Keep track of screws and small parts using containers or trays.
- Final Cleanup:
- Inspect all disassembled parts for damage or wear.
- Clean the workspace and organize components for easy access during reassembly.
Following these steps will help ensure a systematic approach to dismantling, minimizing the risk of damage and facilitating a smoother reassembly process.
Inspecting Engine Components

When maintaining high-performance machinery, a thorough evaluation of various parts is crucial for optimal functionality. This section focuses on the importance of assessing critical elements to ensure reliability and efficiency. Regular inspections help identify wear and tear, preventing potential failures during operation.
Visual Inspection: Begin with a comprehensive visual check. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or unusual wear on all accessible components. Pay close attention to gaskets, seals, and connections, as leaks can significantly affect performance.
Measurement and Tolerance: Utilize precision tools to measure critical dimensions such as clearances and thicknesses. Comparing these measurements against specified tolerances will indicate whether components are within acceptable limits or require replacement.
Testing for Integrity: Conduct pressure tests and leak-down tests to evaluate the integrity of cylinders and associated systems. This will help ascertain the condition of seals and gaskets, ensuring they maintain proper function under stress.
Component Assessment: Inspect vital parts such as pistons, rods, and bearings for signs of wear. Any irregularities can lead to diminished performance, so it’s essential to address these issues promptly.
Documentation: Keep detailed records of inspections and any findings. This information is invaluable for tracking performance trends and planning future maintenance activities.
Rebuilding the Cylinder Head
The process of overhauling the upper part of a combustion unit is crucial for restoring performance and ensuring longevity. This component plays a vital role in the overall function, and a thorough refurbishment can significantly enhance efficiency and power output.
Essential Steps for Overhaul

To achieve optimal results, follow these key steps:
- Remove the component from the block carefully, ensuring no damage occurs during the disassembly.
- Inspect for cracks or warping, using precision tools to check for flatness.
- Clean all surfaces thoroughly to eliminate carbon deposits and debris.
- Replace worn valves, guides, and seals as necessary to maintain proper sealing and airflow.
- Resurface the mating surface to ensure a perfect fit upon reinstallation.
- Reassemble using high-quality gaskets and fasteners to prevent leaks and failures.
Common Issues to Address
While overhauling the upper section, keep an eye out for frequent problems:
- Cracked or damaged ports can lead to poor performance.
- Worn valve seats may affect compression ratios.
- Overheating can cause significant warping.
- Oil leaks often stem from degraded seals or gaskets.
By focusing on these areas and following a structured approach, the overhaul of the upper section can lead to significant improvements in performance and reliability.
Timing Belt Replacement Guide
Replacing the timing belt is a crucial maintenance task that ensures the proper functioning of your vehicle’s internal mechanisms. This procedure involves meticulous attention to detail and an understanding of the components involved. Following a systematic approach can help avoid costly damage and prolong the lifespan of the powertrain.
Tools and Materials Needed
Before starting the replacement process, gather the following tools and materials:
| Tool/Material | Description |
|---|---|
| Socket Set | A complete set of sockets to fit various fasteners. |
| Torque Wrench | For ensuring bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. |
| Timing Belt | A new belt designed to fit your specific model. |
| Crankshaft Pulley Tool | To help remove and install the crankshaft pulley. |
| Fluid Drain Pan | To catch any fluids that may spill during the process. |
Replacement Procedure
1. Start by disconnecting the battery and draining any necessary fluids to prevent spills.
2. Remove any components obstructing access to the timing belt cover, such as the radiator or air intake.
3. Mark the alignment of the camshaft and crankshaft pulleys to ensure proper reinstallation.
4. Loosen and remove the old timing belt, taking care to avoid disturbing the adjacent components.
5. Install the new timing belt, ensuring it is aligned correctly with the marked positions.
6. Reassemble all previously removed parts, making sure to follow the proper torque specifications.
7. Finally, reconnect the battery and check for proper operation.
Turbocharger Maintenance Tips

Proper upkeep of your turbocharging system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention to its components can prevent issues that may lead to costly repairs and decreased efficiency. Here are some key practices to ensure your turbocharger remains in excellent condition.
Regular Inspections
Routine checks are vital. Inspect the turbocharger for signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Look for oil leaks around the unit and listen for any unusual noises during operation. Catching problems early can save time and money.
Oil Quality and Levels

Maintaining the correct oil levels and using high-quality lubricants are crucial. The oil lubricates and cools the turbo, reducing friction and heat buildup. Ensure you change the oil regularly and use a filter that meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Every 5,000 miles |
| Oil Change | Every 5,000 miles or as recommended |
| Boost Pressure Check | Every 10,000 miles |
Following these maintenance tips can help ensure your turbocharger operates efficiently, providing you with the performance you expect while minimizing the risk of breakdowns.
Fuel System Repairs Explained
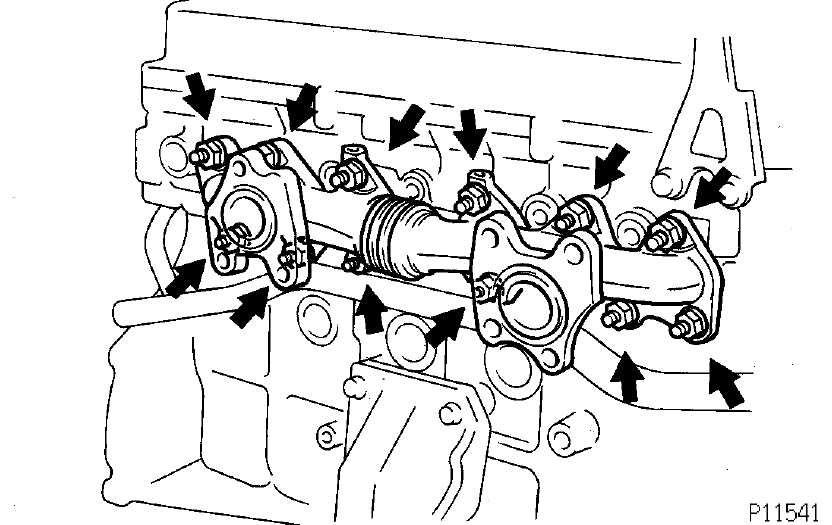
The fuel system plays a critical role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. Understanding how to address common issues within this system can lead to improved functionality and longevity. This section delves into essential components, troubleshooting steps, and effective solutions to common fuel delivery problems.
Key Components and Their Functions

At the heart of the fuel system are several vital elements: the fuel pump, injectors, and filters. The fuel pump is responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the combustion area, while the injectors deliver the precise amount of fuel needed for optimal combustion. Additionally, filters ensure that any contaminants are removed before the fuel reaches the injectors, preventing potential damage.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When faced with performance issues, several symptoms can indicate problems within the fuel system. Symptoms such as poor acceleration, rough idling, or decreased fuel efficiency may signal the need for attention. Conducting a thorough diagnosis involves checking fuel pressure, inspecting the injectors for clogs, and ensuring that filters are clean. Addressing these areas promptly can restore proper function and enhance overall performance.
Electrical Diagnostics for 1JZ GTE
Accurate troubleshooting of electrical components is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and reliability. This section provides a systematic approach to identifying and resolving electrical issues that may arise, ensuring that all systems function harmoniously.
Begin by gathering essential diagnostic tools, such as a multimeter and an oscilloscope. Familiarize yourself with the electrical schematics to understand the circuitry and flow of current throughout the system.
| Component | Common Issues | Diagnostic Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | Weak charge, corrosion | Measure voltage; clean terminals |
| Alternator | Poor output, noise | Check output voltage; inspect belt tension |
| Sensors | Faulty readings | Test resistance; verify signal output |
| Wiring Harness | Frayed wires, shorts | Inspect visually; perform continuity tests |
| Fuses | Blown, intermittent issues | Check for continuity; replace as needed |
When performing diagnostics, document all findings and steps taken. This record aids in understanding patterns and can be invaluable for future reference. With a methodical approach, you can ensure that electrical anomalies are addressed efficiently and effectively.
Reassembly Techniques and Best Practices

When restoring mechanical components, precision and attention to detail are paramount. Proper techniques during reassembly ensure longevity and optimal performance of the unit. This section outlines key practices and methods to follow for a successful assembly process.
Preparation and Organization

Before starting the reassembly, it’s crucial to prepare the workspace and organize all components. This reduces the risk of misplacing parts and helps in identifying necessary tools. A clean and well-lit area will facilitate a smoother workflow.
Step-by-Step Assembly
Following a systematic approach can significantly enhance the reassembly process. Here are some best practices:
| Step | Description | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inspect all components for wear or damage. | Replace any worn or damaged parts before assembly. |
| 2 | Refer to documentation for torque specifications. | Use a torque wrench to ensure proper tightness. |
| 3 | Apply lubricants to moving parts as specified. | Ensure all surfaces are clean before lubrication. |
| 4 | Assemble components in the reverse order of disassembly. | Keep track of each part to avoid confusion. |
| 5 | Conduct a final inspection after assembly. | Look for any loose fittings or misplaced parts. |
By adhering to these techniques, the likelihood of issues arising during operation can be minimized, ultimately contributing to the durability and efficiency of the unit.
Testing Engine Performance After Repair

Evaluating the functionality of a power unit post-maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal operation and longevity. This process involves various assessments to verify that the necessary adjustments and replacements have been executed correctly. By systematically analyzing the performance metrics, one can identify any lingering issues and confirm that the vehicle meets its intended performance standards.
Performance Assessment Procedures
The initial step in the evaluation process involves a thorough visual inspection for any signs of leaks or irregularities. Following this, conducting a series of diagnostic tests is essential. Utilizing specialized tools can help monitor parameters such as pressure, temperature, and emissions. These readings provide valuable insights into the system’s overall health and efficiency.
Road Testing and Data Analysis

Once the diagnostic checks are complete, it’s time to perform a road test. This practical assessment allows for real-world evaluation of responsiveness, power delivery, and overall drivability. Collecting data during this phase is vital, as it offers a direct comparison to pre-maintenance performance. Analyzing the collected data will highlight any areas that require further attention, ensuring that the power unit operates at peak efficiency.