Comprehensive Guide to Repairing the Toyota 3S-FE Engine

In the realm of automotive maintenance, understanding the intricacies of specific components is vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This guide delves into the nuances of a particular model’s internal workings, providing valuable insights into troubleshooting and enhancement. Whether you are an experienced mechanic or a novice enthusiast, mastering these details can greatly improve your vehicle’s functionality.
Precision is crucial when addressing mechanical issues. Each segment of the assembly plays a significant role, and recognizing the interdependencies can lead to more effective diagnostics. This resource emphasizes not only the common pitfalls but also the best practices for tackling various challenges that may arise during maintenance.
Moreover, the importance of regular upkeep cannot be overstated. By following a structured approach to inspections and modifications, you can mitigate potential failures and maintain peak efficiency. This compilation serves as a foundational reference, offering step-by-step guidance and essential tips to facilitate a thorough understanding of the operational mechanics involved.
Overview of the 3S-FE Powertrain

This section provides a comprehensive insight into a popular inline-four configuration that has been widely utilized in various vehicles. Known for its balance of performance and efficiency, this power unit is a favored choice among enthusiasts and mechanics alike.
Characterized by its robust design, this power unit features several notable attributes:
- Type: Inline-four configuration
- Displacement: Approximately 2.0 liters
- Valvetrain: Dual overhead camshaft (DOHC) setup
- Fuel System: Electronic fuel injection for enhanced efficiency
Performance specifications often include:
- Power Output: Ranges typically from 130 to 145 horsepower
- Torque: Offers a substantial torque range, making it suitable for various driving conditions
This power unit is often lauded for its reliability and ease of maintenance, making it a popular option for both daily driving and performance applications. Understanding its components and functioning can greatly aid in troubleshooting and optimizing performance.
Common Issues and Symptoms

Understanding the typical problems that can arise in a specific automotive system is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity. Identifying these issues early can prevent extensive damage and costly repairs. Below are some common symptoms associated with this particular configuration.
Common Problems
- Overheating: Excessive heat can lead to various complications, including warped components.
- Oil Leaks: Noticeable fluid spots under the vehicle may indicate compromised seals or gaskets.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A significant drop in efficiency can suggest issues with fuel delivery or combustion.
- Rough Idling: Inconsistent engine speed while stationary may indicate problems with the ignition or air-fuel mixture.
- Unusual Noises: Knocking or tapping sounds can signal internal wear or loose components.
Symptoms to Watch For

- Check Engine Light: Activation of this warning can indicate a range of underlying issues.
- Exhaust Smoke: Varying colors of smoke can provide insights into specific problems; blue smoke often signifies oil burning, while black smoke indicates excessive fuel.
- Vibration: Unexplained shaking during operation may point to misalignment or worn mounts.
- Difficulty Starting: Persistent starting issues can be related to electrical or fuel system failures.
Tools Required for Repair

When undertaking mechanical tasks, having the right instruments is essential for achieving optimal results. A well-equipped toolkit not only enhances efficiency but also ensures precision during the process. This section outlines the necessary tools that will facilitate the restoration and maintenance of the specific vehicle type in question.
Essential Hand Tools
A variety of hand tools is indispensable for any mechanical endeavor. Basic items include wrenches, pliers, and screwdrivers in various sizes, which allow for the loosening and tightening of components. Additionally, a torque wrench is crucial for ensuring that fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications, preventing future issues.
Specialized Equipment
In addition to standard hand tools, specialized equipment may be required for more complex tasks. A diagnostic scanner can aid in identifying issues by reading error codes from the onboard computer. Furthermore, a jack and jack stands are necessary for safely lifting the vehicle, providing access to the undercarriage for inspection and servicing.
Disassembly Process Explained
The disassembly of a power unit requires careful planning and execution to ensure all components are handled properly. This section provides a structured approach to the dismantling process, emphasizing the importance of organization and precision.
Before beginning, gather the necessary tools and materials:
- Wrenches and sockets
- Screwdrivers (flat and Phillips)
- Pliers
- Torque wrench
- Container for small parts
- Cleaning supplies
Follow these steps to systematically disassemble the unit:
- Preparation: Disconnect the power source and ensure a clean working area.
- Remove ancillary components: Take off accessories such as the intake manifold, exhaust manifold, and any connected parts.
- Detach the block: Carefully unbolt the main assembly, ensuring no bolts are stripped or damaged.
- Inspect and label parts: As each component is removed, inspect for wear and tear. Label and store them in an organized manner for reassembly.
- Clean surfaces: Use appropriate cleaning agents to remove grime and debris from the surfaces before proceeding further.
Adhering to this structured approach will facilitate a smooth disassembly, making it easier to diagnose issues and prepare for the reassembly process.
Inspecting Engine Components
Regular examination of various parts is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of the power unit. Identifying wear, damage, or any irregularities can prevent significant issues down the road and ensure efficient operation.
Key Areas to Examine

- Cylinders: Check for signs of scoring or abnormal wear.
- Pistons: Look for cracks, excessive carbon buildup, or surface damage.
- Valves: Inspect for proper sealing and any signs of erosion or bending.
- Timing Belt: Ensure there are no frays or cracks, and check tension levels.
- Gaskets: Look for leaks or deterioration that may cause loss of compression.
Inspection Process
- Start by cleaning the surface of each component to get a clear view.
- Use a flashlight to inspect hard-to-see areas and check for any abnormalities.
- Measure tolerances with appropriate tools to ensure all parts meet specifications.
- Document any findings and determine if replacement or further servicing is necessary.
Thoroughly inspecting these crucial elements not only aids in immediate performance but also contributes to the overall health of the machinery over time.
Rebuilding the Cylinder Head
Reconstructing the top section of a motor is a critical process that requires precision and attention to detail. This phase involves disassembling, inspecting, and reconditioning various components to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper techniques and tools are essential to achieve a successful rebuild that restores functionality and reliability.
Inspection and Preparation
Before beginning the reconstruction, a thorough examination of the cylinder head is crucial. This step includes checking for cracks, warping, and other signs of wear. Cleaning the surface and components ensures that any debris or contaminants are removed, facilitating better sealing and performance.
Reconditioning Process

After inspection, the next step is to recondition various elements such as valves, springs, and guides. Each part must be meticulously worked on to meet manufacturer specifications. The following table outlines common tasks involved in the reconditioning process:
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Valves Refacing | Resurfacing valves to ensure a proper seal and reduce leaks. |
| Spring Replacement | Replacing worn-out springs to maintain proper pressure and performance. |
| Guide Inspection | Checking and replacing guides to ensure valve alignment and stability. |
| Surface Resurfacing | Flattening the mating surface to ensure a tight fit with the block. |
By following these steps and utilizing the right tools, the top section can be successfully rebuilt, enhancing the overall performance of the vehicle.
Replacing Timing Belt Steps
Replacing the timing belt is a crucial maintenance task that ensures the proper functioning of the vehicle’s internal components. A worn or damaged belt can lead to significant engine issues, making it essential to follow a systematic approach to this process.
Preparation and Tools Needed

Before starting the replacement, gather all necessary tools, including a socket set, torque wrench, and belt tension gauge. Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface, and disconnect the battery to prevent any electrical issues. It’s also advisable to consult the specific guidelines for your vehicle model for any unique requirements.
Step-by-Step Replacement Process
Begin by removing the protective covers to access the timing mechanism. Rotate the crankshaft to align the timing marks on the pulleys, ensuring the correct position for the new belt installation. Carefully remove the old belt, taking note of the routing path. Install the new belt, making sure it is taut but not overly tight, and double-check the alignment with the timing marks. Once everything is in place, reattach the covers and reconnect the battery.
Final Check: After installation, turn the crankshaft manually to ensure smooth operation before starting the vehicle. This helps verify that the belt is correctly aligned and functioning as intended.
Fuel System Maintenance Tips

Proper upkeep of the fuel delivery system is crucial for optimal vehicle performance. Regular maintenance not only ensures efficient operation but also prolongs the lifespan of critical components. Implementing a few essential practices can significantly enhance the reliability of your fuel system.
Start by routinely checking and replacing the fuel filter, as a clogged filter can restrict fuel flow and lead to performance issues. Inspect fuel lines for leaks or wear, as even minor damage can cause serious problems over time. Additionally, cleaning or replacing fuel injectors can improve fuel atomization and combustion efficiency.
Using high-quality fuel can also make a noticeable difference in performance and engine cleanliness. Avoiding fuel blends that contain excessive alcohol or contaminants is advisable, as they can lead to deposits and clogging. Furthermore, consider adding fuel system cleaners periodically to help maintain injector cleanliness and prevent build-up.
Lastly, keep an eye on fuel pressure levels to ensure they remain within manufacturer specifications. Low pressure can indicate issues such as a failing fuel pump or a blocked line, while excessively high pressure may lead to injector failure. Regular diagnostics can help identify these problems early, allowing for timely intervention.
Checking Electrical Connections
Ensuring the reliability of power transmission is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of a vehicle’s components. Regular inspection of electrical links helps identify potential issues, such as corrosion, wear, or loose contacts, which can lead to malfunctioning systems.
Visual Inspection
Begin by visually examining all accessible connections. Look for signs of damage, such as frayed wires or burnt terminals. Pay special attention to areas exposed to moisture or heat, as these conditions can accelerate degradation. If any irregularities are noticed, consider replacing the affected parts to prevent further complications.
Testing Continuity
After the visual check, utilize a multimeter to assess continuity across connections. Set the device to the appropriate setting and touch the probes to either side of the connection. A reading close to zero indicates a solid link, while a higher resistance suggests an issue that needs to be addressed. Regular continuity checks can help maintain a healthy electrical system.
Reassembly Guidelines to Follow
Reassembling a complex mechanism requires careful attention to detail and adherence to specific procedures. This section outlines essential steps and considerations to ensure successful reconstruction of the components involved.
Before starting, gather all necessary tools and parts. Make sure the workspace is clean and organized to prevent losing small items. Reviewing the disassembly notes can provide valuable insights into the order and orientation of each component.
Begin the process by applying appropriate lubrication to moving parts. This will facilitate smoother operation and reduce wear. Follow the recommended torque specifications for bolts and fasteners to avoid damage or malfunction.
As you assemble, double-check that all seals and gaskets are properly positioned to prevent leaks. Pay special attention to any alignment marks or indicators that guide the placement of parts. Ensuring proper alignment is crucial for optimal performance.
Finally, perform a thorough inspection once reassembly is complete. Verify that all connections are secure and that there are no leftover components. Conduct a test run to confirm functionality and address any issues that may arise.
Testing Engine Performance Post-Repair
After any significant overhaul or service of an automotive power unit, it is crucial to evaluate its functionality and efficiency. This process ensures that all modifications have been executed properly and that the unit operates smoothly under various conditions. By conducting thorough assessments, one can identify potential issues and verify the success of the maintenance work performed.
Begin by performing a comprehensive diagnostic check using appropriate tools to assess key performance metrics. Monitoring parameters such as power output, fuel consumption, and emissions will provide valuable insights into the current state of the unit. Additionally, road tests should be conducted to observe how the vehicle responds under different driving scenarios, ensuring that it meets expected standards.
Furthermore, visual inspections can reveal signs of potential complications, such as leaks or unusual noises, which might indicate underlying problems. Regular monitoring and data analysis will aid in tracking performance trends over time, facilitating early detection of any deviations from optimal functionality.
Ultimately, these evaluations not only confirm the effectiveness of the servicing but also enhance the longevity and reliability of the power unit, ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience.
Preventive Maintenance for Longevity
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the durability and efficiency of any mechanical system. By implementing a consistent maintenance schedule, owners can significantly extend the lifespan of their vehicles while minimizing unexpected breakdowns. Proactive care not only enhances performance but also contributes to overall safety and reliability.
Key Practices for Effective Care
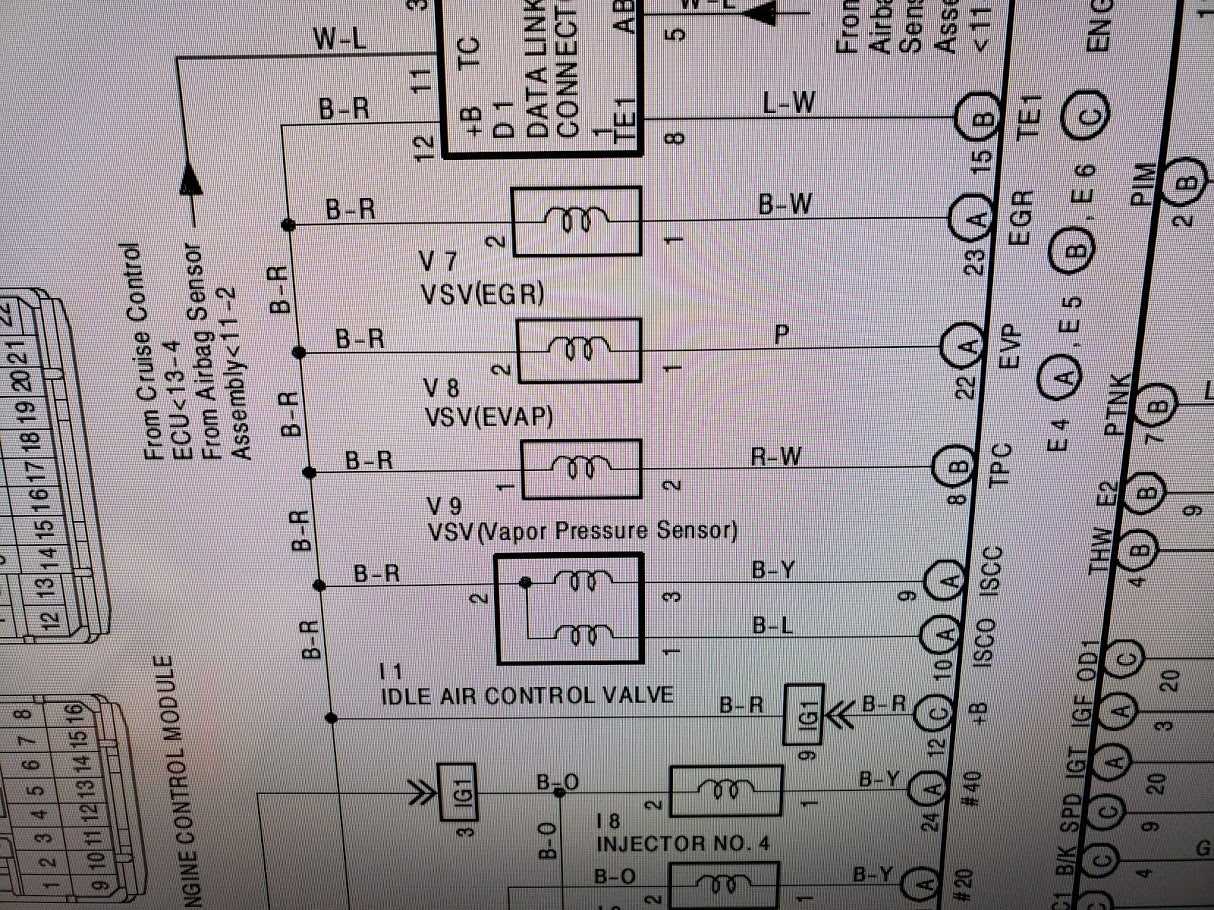
One of the most crucial aspects of effective upkeep involves routine inspections. Checking fluid levels, including oil, coolant, and transmission fluid, is vital. Additionally, examining belts and hoses for signs of wear can prevent potential issues before they escalate. Regularly replacing filters ensures optimal operation and promotes a cleaner environment within the system.
Importance of Timely Interventions

Addressing minor issues promptly is a hallmark of good maintenance practices. Ignoring small leaks or unusual noises can lead to more significant problems and costly repairs. Scheduling periodic professional evaluations allows for comprehensive assessments and expert advice, ensuring all components function harmoniously. Prioritizing these practices ultimately leads to a smoother driving experience and a more resilient vehicle.