Guide to Restoring Wire Connections for Toyota Vehicles

Dealing with interconnected components in modern machinery demands a methodical approach to ensure optimal performance. Understanding how these elements are routed and maintained helps prevent operational failures and extends the equipment’s lifespan. This section focuses on the essential practices for maintaining these intricate systems effectively.
The following guide covers key strategies for addressing common issues found in electrical connections, emphasizing both preventive measures and corrective solutions. By following structured instructions, one can restore functionality to complex systems, minimizing downtime.
Whether handling routine adjustments or resolving more intricate malfunctions, the insights provided here offer practical methods for identifying, isolating, and fixing disruptions. Ensuring stable performance requires attention to detail, a clear understanding of the components involved, and the ability to apply proper maintenance techniques efficiently.
This guide is designed for those seeking practical solutions, providing a well-rounded perspective on how to manage, inspect, and maintain these interconnected assemblies for long-term reliability.
Guidelines for Restoring Electrical Connections
Ensuring proper continuity in circuitry is essential for maintaining optimal performance in any electrical system. Over time, disruptions such as corrosion, loose terminals, or damaged connectors may compromise these connections, leading to malfunctions. Addressing such issues requires attention to detail and a structured approach to restore functionality and prevent future disruptions.
Identifying Faulty Links
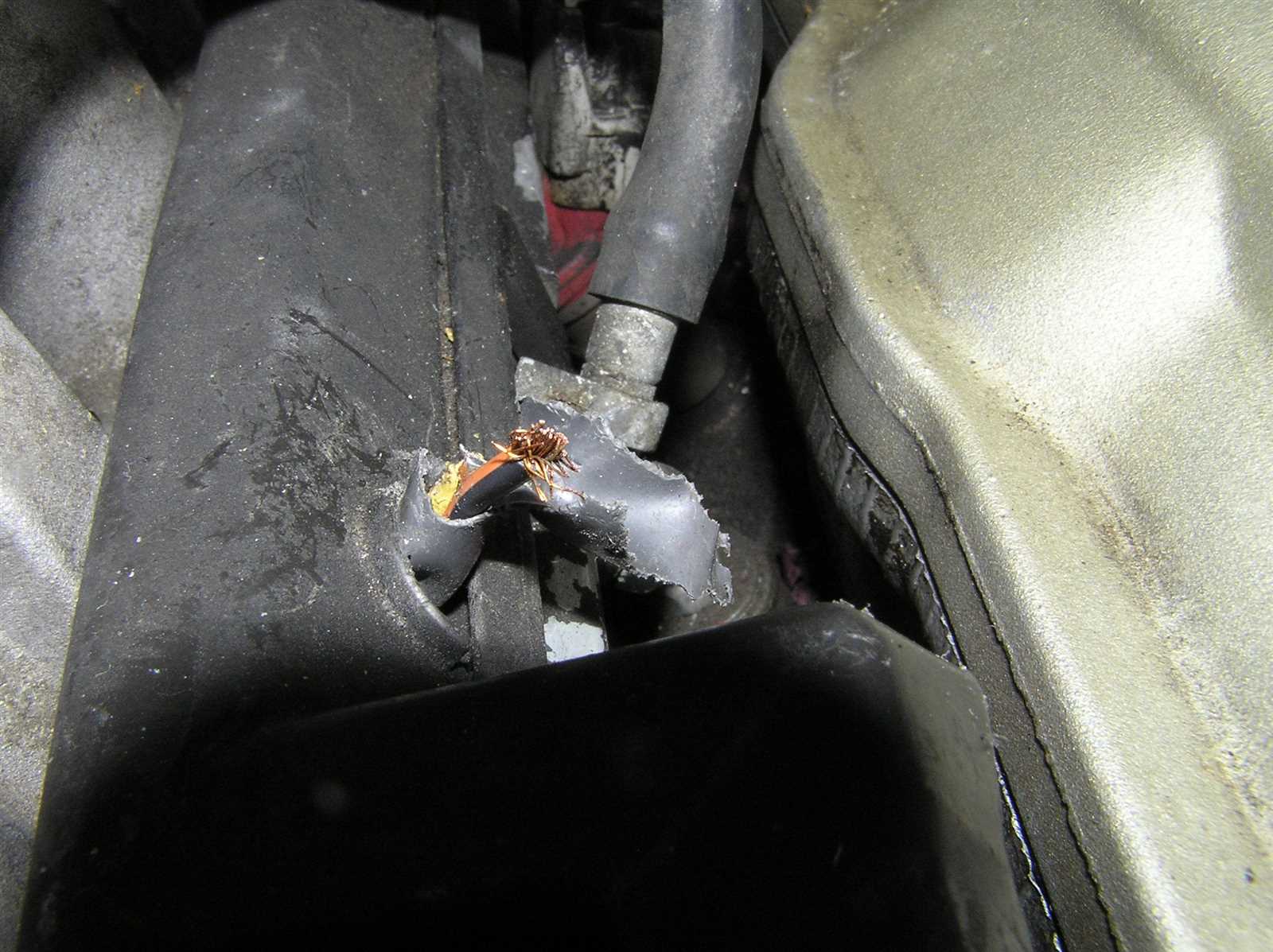
Begin by carefully inspecting each connection for signs of wear, corrosion, or breakage. Look for discoloration or physical damage that might affect current flow. Testing continuity with appropriate instruments ensures that weak or open circuits are identified before reassembly.
Reconditioning Terminals and Contacts
When restoring connections, cleaning and re-tensioning terminals are vital steps. Use contact cleaners or abrasive tools to remove corrosion and restore metal surfaces. Applying conductive grease can further protect connections from future oxidation, enhancing longevity and reliability.
Identifying Common Wiring Faults
Recognizing frequent electrical path issues is essential for maintaining stable connections between system components. Breaks in continuity, signal interference, and misalignments can disrupt functionality, leading to unexpected malfunctions or complete system failure. Identifying these issues early helps prevent further complications and ensures smooth operation.
Typical Symptoms of Electrical Issues
- Intermittent loss of signal or power
- Unusual flickering or dimming of connected devices
- Overheating or strange smells from connectors
- Failure to activate essential components during operation
Key Causes of Connection Problems
- Corroded Contacts: Exposure to moisture or chemicals can degrade connectors, reducing their ability to conduct signals.
- Frayed or Damaged Insulation: Physical wear over time can leave internal strands exposed, increasing the risk of short circuits.
- Poorly Seated Connectors: Misaligned pins or loosely connected terminals can lead to intermittent performance issues.
- Overloaded Circuits: Connecting too many devices to a single pathway may result in overheating and failures.
Proper inspection and timely maintenance are essential to prevent these faults from escalating. Prioritizing diagnostic checks ensures that minor issues are caught early, preserving the overall reliability of the system.
Essential Tools for Harness Repairs
Maintaining electrical pathways requires the right set of tools to ensure secure connections, proper insulation, and reliable functionality. These instruments simplify the troubleshooting process and enable efficient work, minimizing future complications.
Basic Equipment
- Crimping tool: Ensures tight and durable connections between conductors and terminals.
- Stripping tool: Removes insulation without damaging the internal strands.
- Multimeter: Measures continuity, voltage, and resistance for diagnostic purposes.
Advanced Instruments

- Heat gun: Activates shrink tubing to seal exposed areas, preventing moisture intrusion.
- Soldering kit: Provides long-lasting bonds for critical electrical junctions.
- Connector removal tool: Facilitates disassembly of plugs without damaging contacts.
Using the appropriate tools not only saves time but also ensures that the system remains stable and performs optimally under various conditions.
Steps to Diagnose Circuit Breakdowns
Identifying issues in complex electrical systems requires a structured approach to ensure efficient troubleshooting. The process involves carefully evaluating various components, verifying connections, and confirming the functionality of individual segments to detect potential faults.
1. Visual Inspection: Begin by examining connectors, terminals, and related parts for signs of corrosion, damage, or improper alignment. Look for burnt sections, exposed elements, or loose fittings that might interrupt the flow of current.
2. Continuity Check: Use a multimeter to verify uninterrupted paths between components. Confirm that circuits are complete, and there are no unintended breaks or shorts affecting the performance.
3. Component Testing: Evaluate critical parts like fuses and relays to ensure they function as intended. Replace faulty elements if they disrupt the energy flow across the system.
4. Voltage Measurement: Measure power levels at key points within the network. Inconsistent readings could indicate underlying malfunctions or insufficient supply in specific areas.
5. Signal Trace: Follow the expected path of signals, ensuring that each section delivers the correct output. Missing or distorted signals can point to damaged elements or incorrect setups.
By following these diagnostic steps, one can systematically isolate faults and restore optimal system performance.
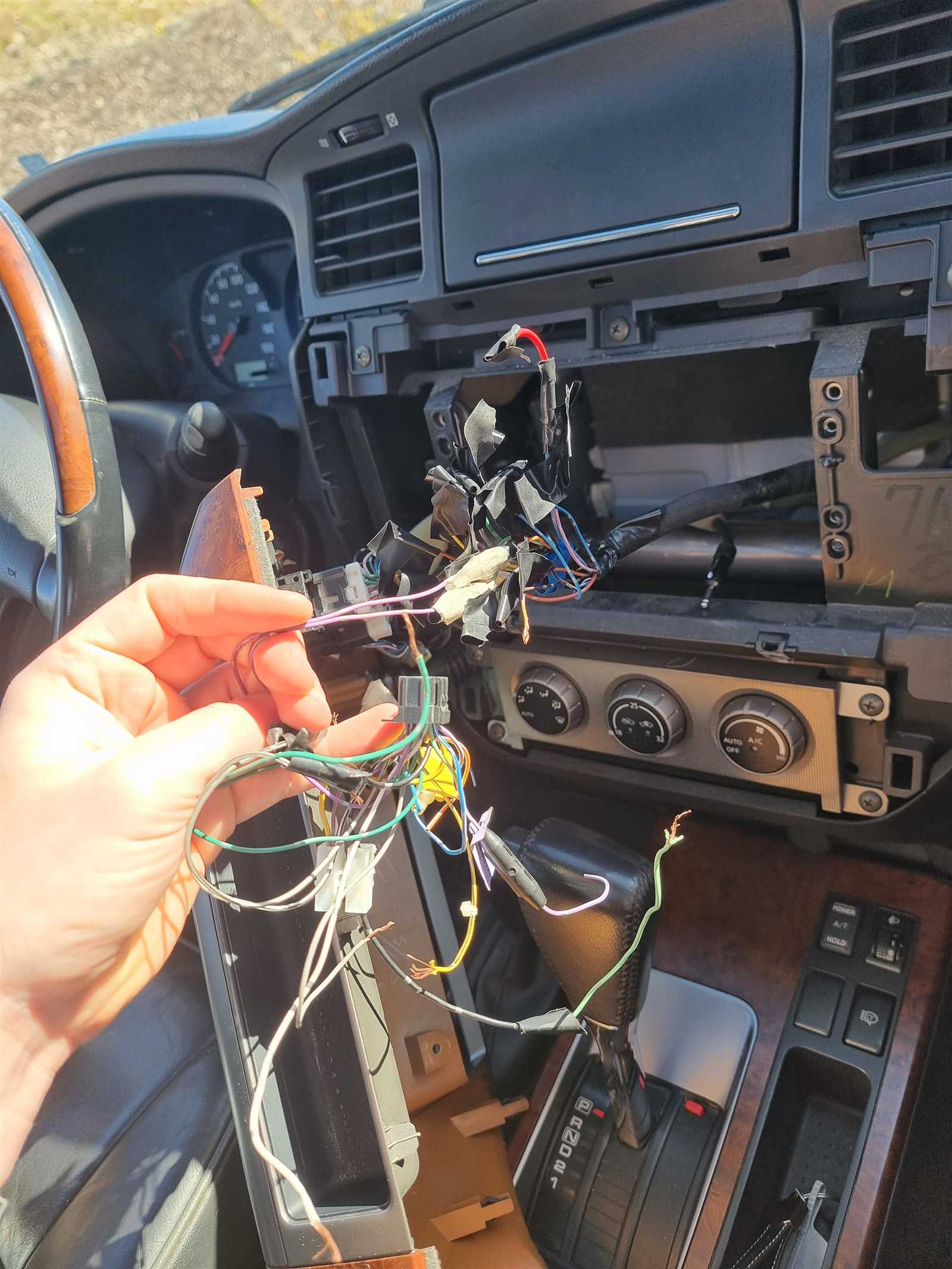
Techniques for Connector Replacements
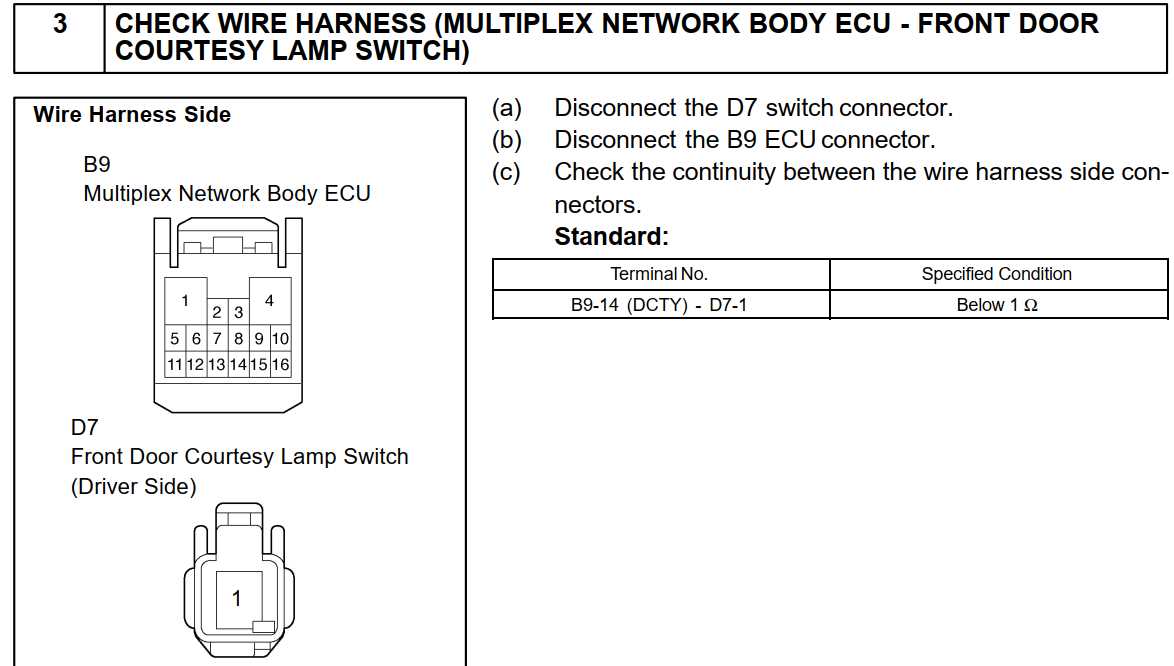
Maintaining reliable connections is essential for ensuring smooth functionality in complex systems. When connectors become worn or damaged, timely replacement can restore optimal performance. Proper techniques allow for seamless transitions, avoiding potential issues caused by poor contact or mismatched components.
Identifying Compatible Components: Before beginning the replacement, it is crucial to select a new connector that matches the original specification. Pin alignment, shape, and electrical characteristics must be considered to ensure compatibility.
Preparation and Disassembly: Disconnecting existing components carefully prevents further damage. Using appropriate tools, connectors should be disassembled without applying excessive force, especially in older or fragile systems.
Assembly and Testing: Once the new part is secured, all connections should be verified to confirm that each terminal fits correctly. After reassembly, thorough testing ensures the newly installed connectors are functioning as expected, preventing future malfunctions.
Proper Soldering Methods for Reliability

Ensuring lasting connections is crucial in any electrical assembly process. The quality of solder joints significantly influences the overall performance and durability of the system. Employing appropriate techniques during the soldering process can mitigate potential issues such as corrosion, mechanical stress, and electrical failures. This section outlines essential practices to achieve reliable soldering results.
Preparation and Cleanliness

Before initiating the soldering process, it is vital to prepare the components and the surface. Begin by cleaning the areas to be joined to remove any dirt, grease, or oxidation. Utilizing a suitable solvent or abrasive can enhance the quality of the bond. Additionally, ensuring that the components are securely positioned prevents movement during solder application, leading to stronger joints.
Temperature Control and Technique

Maintaining the correct temperature during soldering is essential for achieving a reliable connection. Excessive heat can damage components, while insufficient heat may lead to weak joints. It is advisable to use a soldering iron with a temperature control feature. When applying solder, use a technique that promotes even distribution; a small amount of solder should flow smoothly into the joint, forming a strong and clean bond. Practicing these methods will significantly enhance the longevity and performance of electrical assemblies.
Protecting Wires from Heat and Moisture
Safeguarding electrical connections from extreme temperatures and humidity is crucial for maintaining functionality and longevity. Proper insulation and protective measures ensure that conductive elements remain operational, preventing potential failures and hazards.
Effective strategies for shielding these components include:
- Insulation Materials: Utilizing high-quality insulating substances that can withstand elevated temperatures and moisture is essential. Consider options like silicone, rubber, or specialized heat-resistant plastics.
- Heat Shrink Tubing: Applying heat shrink tubing provides an additional layer of protection. It conforms tightly to the surface, creating a waterproof seal that safeguards against moisture ingress.
- Conformal Coatings: Coating exposed surfaces with a conformal material can protect against environmental factors. These coatings provide a barrier that repels moisture while allowing heat dissipation.
- Routing Techniques: Organizing and routing elements away from heat sources can significantly reduce exposure. Ensure that they are not in direct contact with components that generate high temperatures.
By implementing these protective measures, the reliability and safety of electrical systems can be greatly enhanced, minimizing the risk of failures caused by heat and moisture.
Testing Continuity After Repairs
Ensuring a solid connection within electrical systems is crucial for their optimal performance. After making modifications or adjustments to any wiring configurations, it is essential to verify that the flow of electricity is uninterrupted. This section outlines the process of checking for continuity, which helps to identify any potential faults that may arise from the work completed.
Importance of Continuity Testing

Continuity testing is a fundamental procedure that confirms whether an electrical path is intact. By employing a multimeter or a similar testing device, users can easily determine if current can traverse through the connections without any interruptions. This step is vital to prevent malfunctions that could lead to operational failures.
Steps for Conducting Continuity Tests

To effectively conduct a continuity test, follow these steps:
- Turn off the power to the circuit to ensure safety.
- Set the multimeter to the continuity mode, indicated by a sound symbol.
- Connect the leads of the multimeter to both ends of the section being tested.
- Observe the multimeter’s reading; a beep or a low resistance value indicates good continuity.
- If no sound or high resistance is detected, there may be a break in the connection that requires further investigation.
Conducting these tests is a proactive approach to ensuring that all connections are functioning properly, thereby safeguarding the overall performance of the electrical system.
Choosing the Right Wire Gauge

When undertaking electrical projects, selecting an appropriate conductor thickness is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. The size of the conductive material significantly impacts the performance of the entire system, affecting the flow of current and the overall functionality. Understanding the factors that influence the choice of thickness can lead to more reliable and long-lasting connections.
Factors to Consider
Several key elements should guide the decision-making process when determining the suitable conductor size. These include the amount of current that will pass through the material, the distance the current must travel, and the specific environment in which the system will operate. Additionally, accounting for potential voltage drops and heat generation is essential to avoid complications during operation.
Conductor Size Chart
| Current (Amps) | Recommended Gauge | Maximum Length (Feet) |
|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 18 AWG | 100 |
| 10-15 | 16 AWG | 75 |
| 15-20 | 14 AWG | 50 |
| 20-30 | 12 AWG | 30 |
| 30-40 | 10 AWG | 20 |
By carefully evaluating these aspects and utilizing the chart provided, one can confidently choose the right conductor size for their specific application, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Managing Cable Routing in Vehicles

Effective management of electrical pathways is crucial for ensuring the reliability and safety of automotive systems. Proper organization and secure placement of these pathways not only enhance the overall performance of the vehicle but also minimize potential damage from external elements. This section focuses on best practices for arranging these essential components in a manner that promotes efficiency and longevity.
Importance of Proper Arrangement

Careful planning and execution of the arrangement process can prevent common issues such as wear and tear, signal interference, and accidental disconnections. Ensuring that the connections are well-protected and correctly positioned can significantly reduce the risk of malfunctions and increase the lifespan of the electrical systems. Utilizing protective sleeves and fasteners can help maintain order and safeguard these critical components against environmental hazards.
Techniques for Optimal Routing

When routing electrical connections, consider the shortest and most direct pathways to reduce resistance and enhance signal integrity. It is essential to avoid sharp bends and excessive tension that could lead to damage. Additionally, using clips or guides can help secure the connections in place, preventing movement that might result in abrasion or disconnection. Regular inspections of the layout can identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring continuous performance and safety.
Best Practices for Long-Term Durability
Ensuring the longevity of electrical systems is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and safety in various applications. By adopting effective strategies during installation and maintenance, one can significantly enhance the reliability of these systems over time.
Regular Inspections: Conduct routine checks to identify signs of wear or damage. Look for fraying, corrosion, or loose connections that could compromise functionality. Early detection allows for timely interventions and prevents further deterioration.
Proper Insulation: Use high-quality insulating materials to protect against environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and chemicals. Adequate insulation minimizes the risk of short circuits and prolongs the lifespan of components.
Secure Fastenings: Ensure that all connections are tightly secured. Loose fittings can lead to poor conductivity and increased resistance, which may result in overheating and potential failure.
Environmental Considerations: Be mindful of the surroundings where these systems are installed. Extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can accelerate degradation. Utilize protective enclosures or coverings to shield sensitive components.
Utilizing Quality Components: Invest in high-quality materials and components designed for durability. Although they may come at a higher initial cost, they often provide greater reliability and lower maintenance requirements in the long run.
By following these practices, individuals can significantly improve the durability of their electrical systems, ensuring they function effectively and safely throughout their intended lifespan.